A coal foreign object detection method based on cross modal attention fusion
-
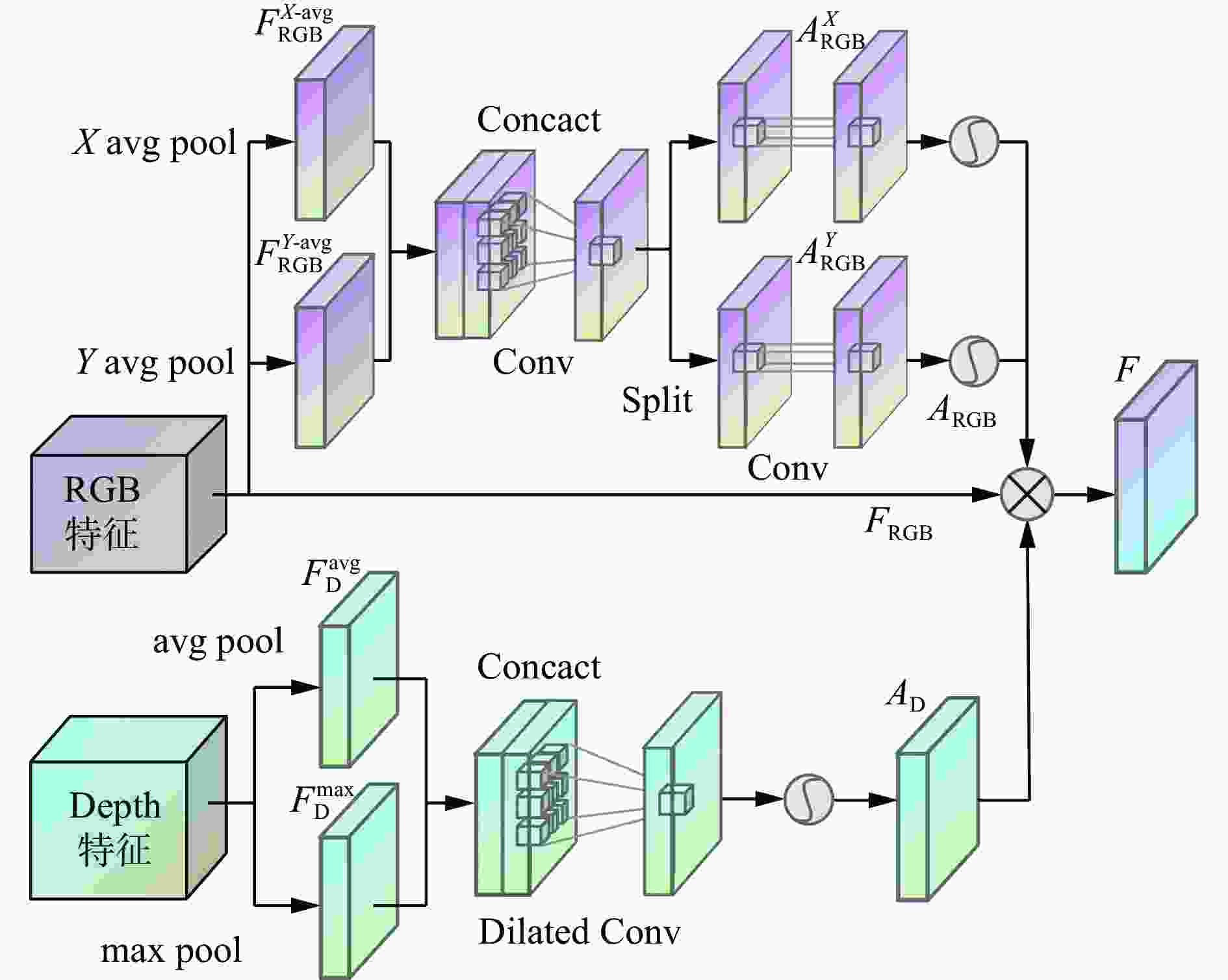
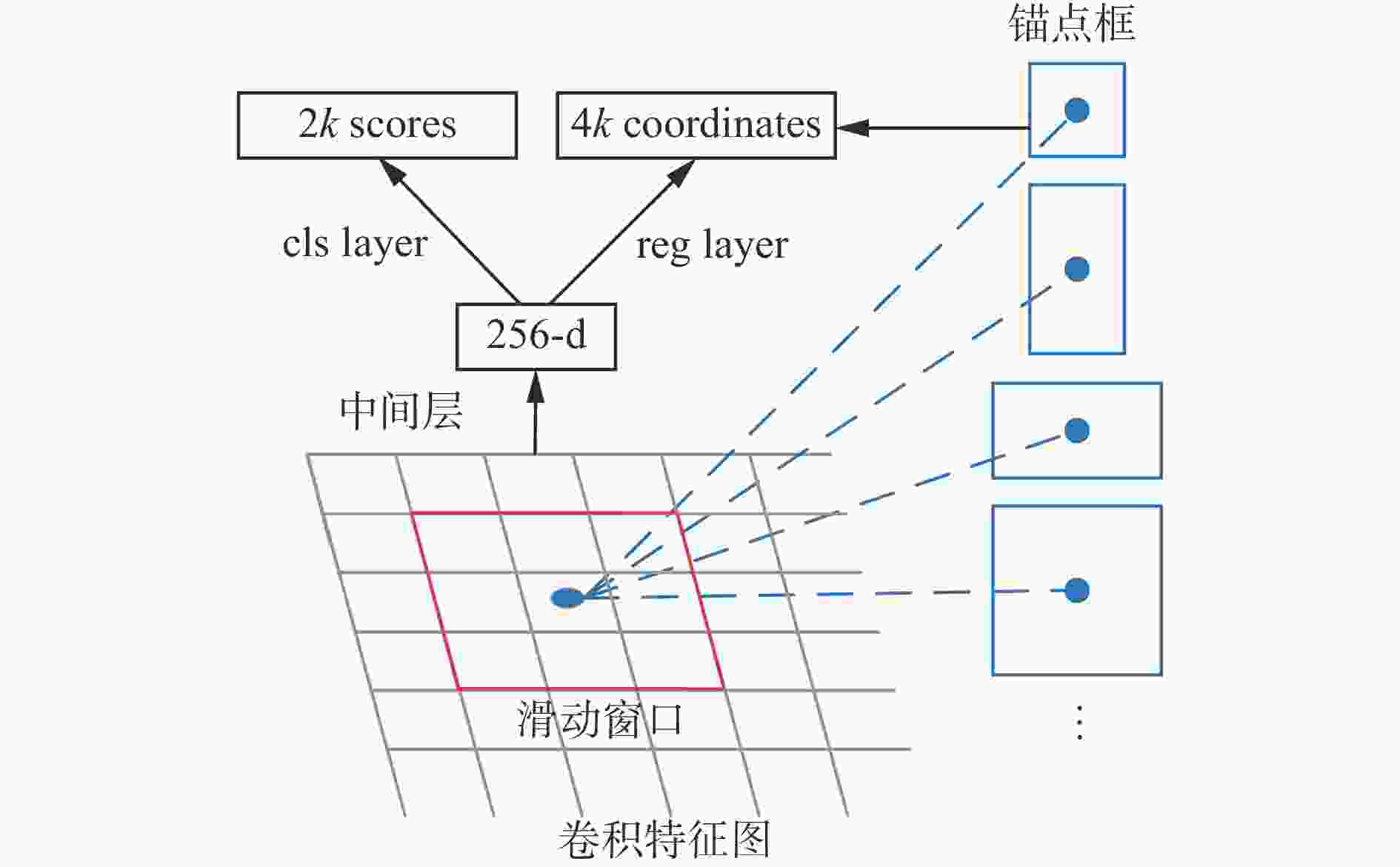
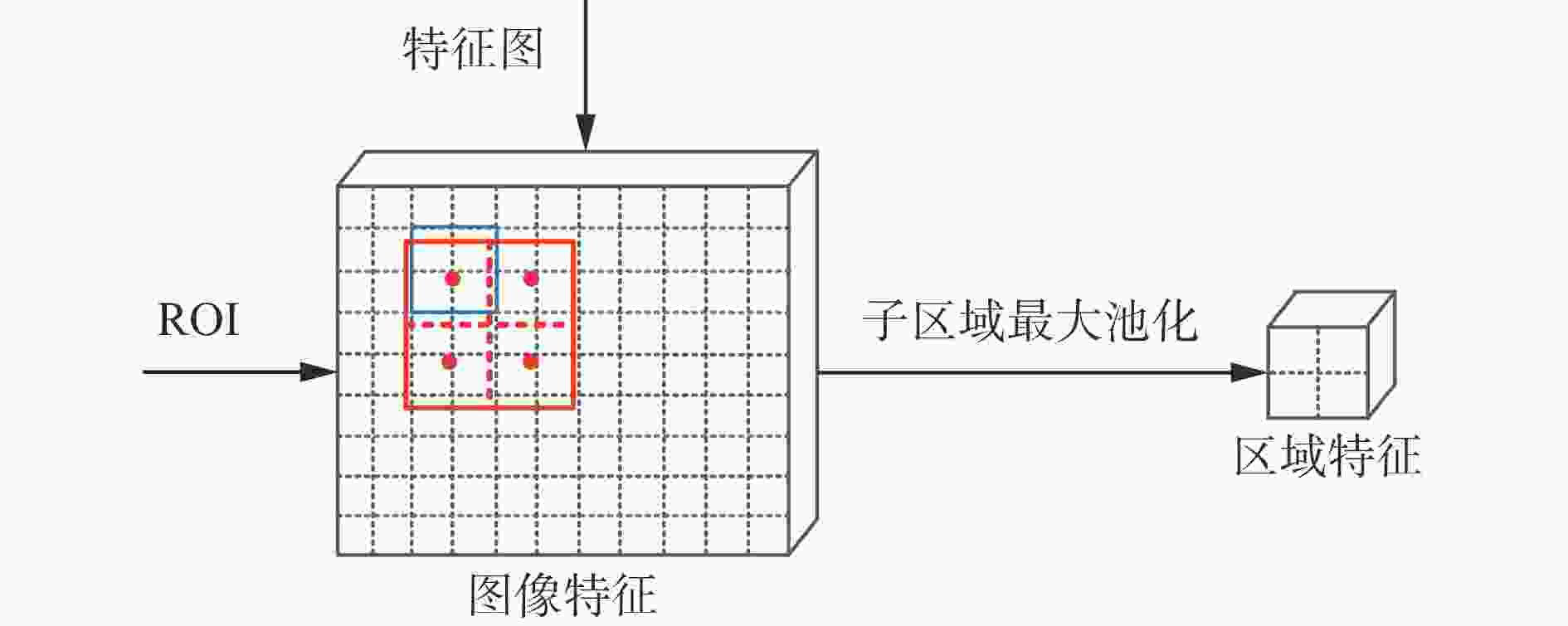
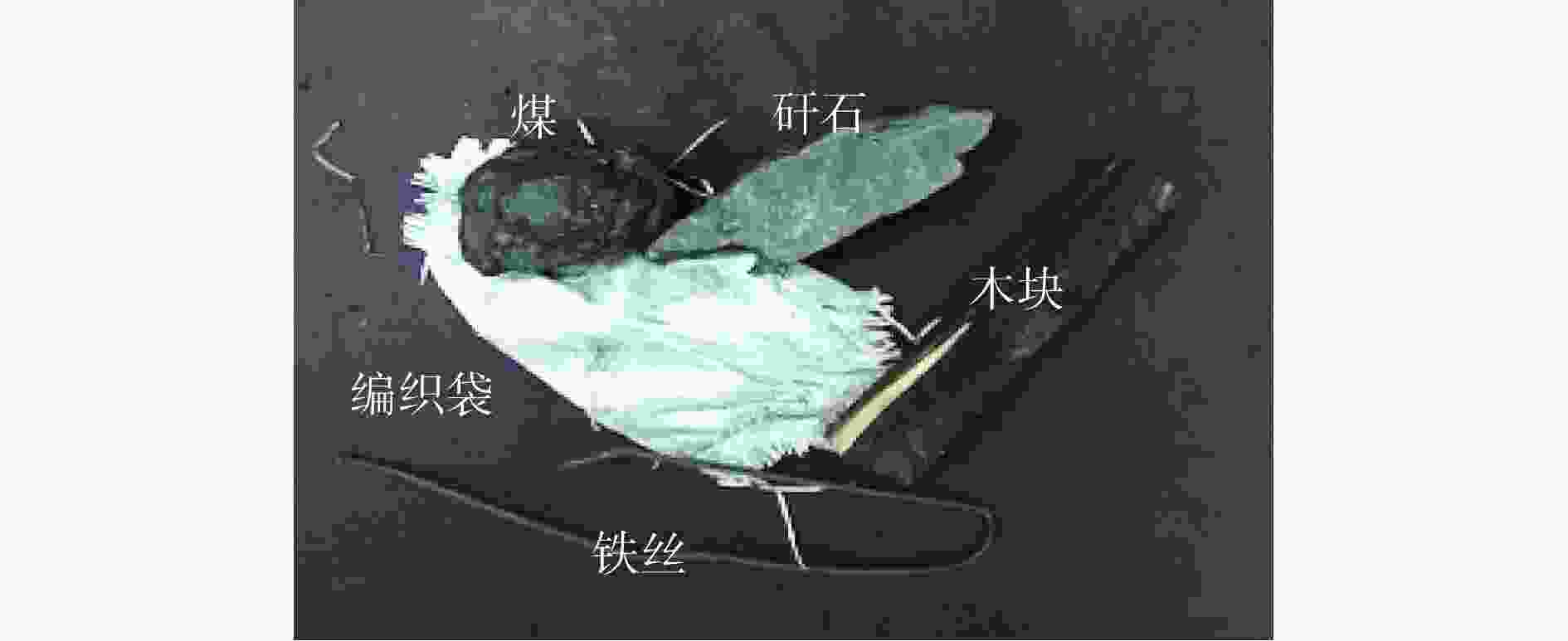
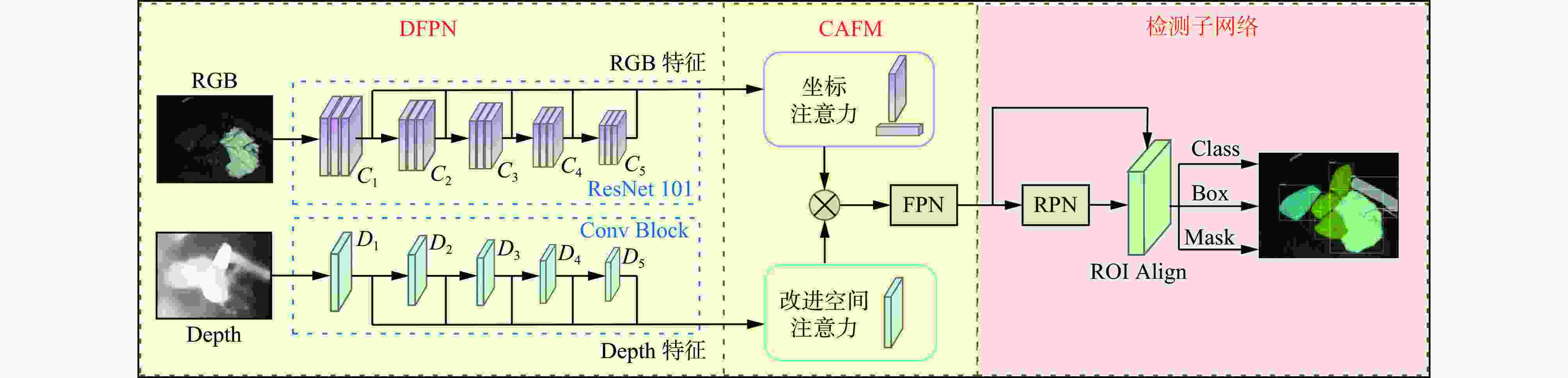
摘要: 为解决原煤智能化洗选过程中煤流中夹杂的异物对比度低、相互遮挡导致异物图像检测时特征提取不充分的问题,提出了一种基于跨模态注意力融合的煤炭异物检测方法。通过引入Depth图像构建RGB图像与Depth图像的双特征金字塔网络(DFPN),采用浅层的特征提取策略提取Depth图像的低级特征,用深度边缘与深度纹理等基础特征辅助RGB图像深层特征,以有效获得2种特征的互补信息,从而丰富异物特征的空间与边缘信息,提高检测精度;构建了基于坐标注意力与改进空间注意力的跨模态注意力融合模块(CAFM),以协同优化并融合RGB特征与Depth特征,增强网络对特征图中被遮挡异物可见部分的关注度,提高被遮挡异物检测精度;使用区域卷积神经网络(R−CNN)输出煤炭异物的分类、回归与分割结果。实验结果表明:在检测精度方面,该方法的AP相较两阶段模型中较优的Mask transfiner高3.9%;在检测效率方面,该方法的单帧检测时间为110.5 ms,能够满足异物检测实时性需求。基于跨模态注意力融合的煤炭异物检测方法能够以空间特征辅助色彩、形状与纹理等特征,准确识别煤炭异物之间及煤炭异物与输送带之间的差异,从而有效提高对复杂特征异物的检测精度,减少误检、漏检现象,实现复杂特征下煤炭异物的精确检测与像素级分割。Abstract: The RGB image of coal foreign objects lacks target space and edge information, the color and texture between the object to be detected and the background are similar, the contrast is low, and there are overlapping and occlusion phenomena among the objects to be detected, resulting in insufficient feature extraction of coal foreign objects, and the existing foreign object detection methods are difficult to achieve ideal results. In order to solve the above problems, a coal foreign object detection method based on cross modal attention fusion is proposed. By introducing Depth images to construct a dual feature pyramid network (DFPN) for RGB images and Depth images, a shallow feature extraction strategy is adopted to extract low-level features of Depth images. Basic features such as deep edges and deep textures are used to assist deep features of RGB images, effectively obtaining complementary information between the two features. It thereby enriches the spatial and edge information of foreign object features and improves detection precision. A cross modal attention fusion module (CAFM) based on coordinate attention and improved spatial attention is constructed to synergistically optimize and fuse RGB features and Depth features. It enhances the network's attention to the visible parts of occluded foreign objects in the feature map, and improves the precision of occluded foreign object detection. Finally, regional convolutional neural network (R-CNN) is used to output the classification, regression, and segmentation results of coal foreign objects. The experimental results show that in terms of detection precision, the average segmentation precision AP of the proposed method is 3.9% higher than the better Mask transformer in the two-stage model. In terms of detection efficiency, the proposed method has a single frame detection time of 110.5 ms, which can meet the real-time requirements of foreign object detection. The coal foreign object detection method based on cross modal attention fusion can assist color, shape, and texture features with spatial features. It accurately recognizes the differences between coal foreign objects and between coal foreign objects and conveyor belts, effectively improves the detection precision of complex feature foreign objects. It reduces false alarms and missed detections, and achieves precise detection and pixel level segmentation of coal foreign objects under complex features.
-
表 1 RGB图像与Depth图像特征提取网络总体结构
Table 1. The overall structure of feature extraction networks for RGB and Depth images
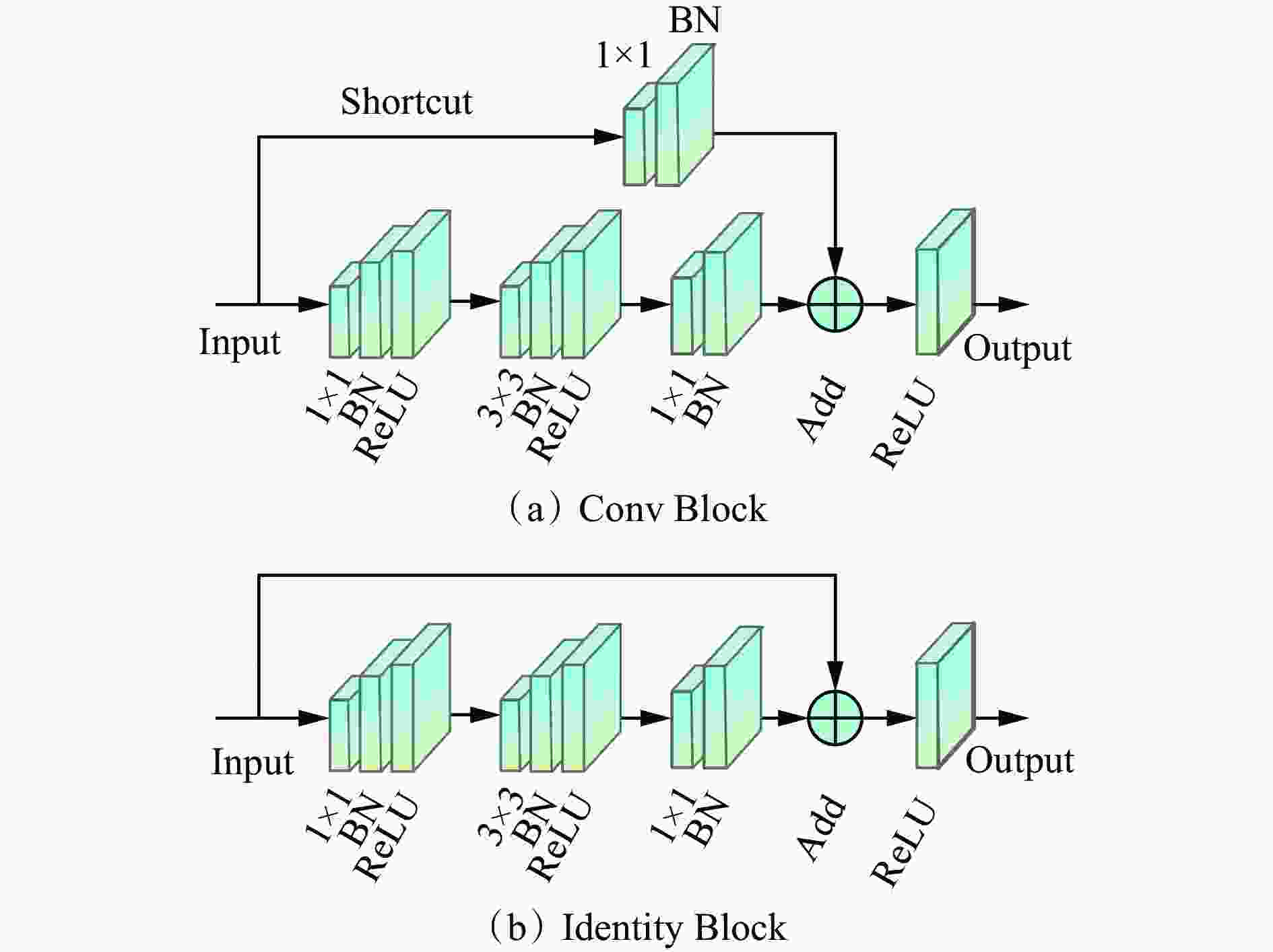
层名 RGB分支 Depth分支 输出通道数 L1 7×7,64,stride 2 64 L2 3×3,max pool,stride 2 256 Conv Block×1
Identity Block×2Conv Block×1 L3 Conv Block×1
Identity Block×3Conv Block×1 512 L4 Conv Block×1
Identity Block×22Conv Block×1 1024 L5 Conv Block×1
Identity Block×2Conv Block×1 2048 表 2 特征提取消融实验结果
Table 2. Ablation experiments results for feature extraction
% Backbone AP AP0.5 AP0.75 APS APM APL RGB Depth ResNet50 ResNet50 72.2 92.3 81.7 28.1 55.6 78.1 ResNet101 70.9 91.5 80.1 27.8 55.2 77.6 Conv Block 76.3 93.2 86.8 29.9 59.1 79.7 ResNet101 ResNet50 74.3 93 83.7 28.7 57.4 78.6 ResNet101 73.7 92.7 82.3 29 56.6 78.3 Conv Block 78.5 94.1 88.1 30.4 60.7 81.7 表 3 特征融合消融实验结果
Table 3. Ablation experiments results for feature fusion
% 融合方式 Backbone AP AP0.5 AP0.75 APS APM APL RGB ResNet101 70.6 91.0 79.1 27.7 54.1 76.2 数据层融合 ResNet101 64.7 87.3 72.2 25.5 50.2 69.9 特征层融合 ResNet101+Conv Block 78.5 94.1 88.1 30.4 60.4 81.7 CAFM ResNet101+Conv Block 82.2 98.9 95.7 32.1 62.5 86.6 表 4 不同模型检测性能对比
Table 4. Comparison of detection performance of different models
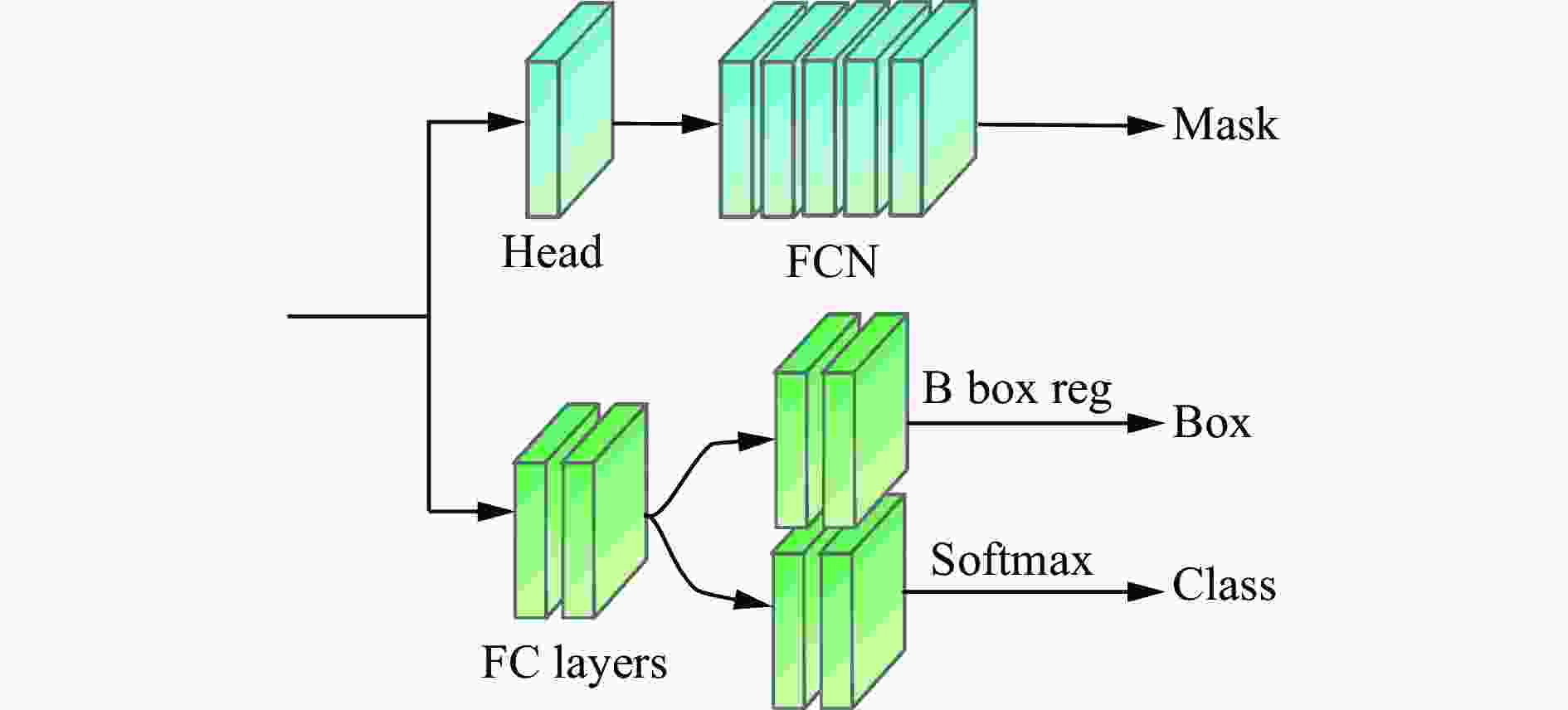
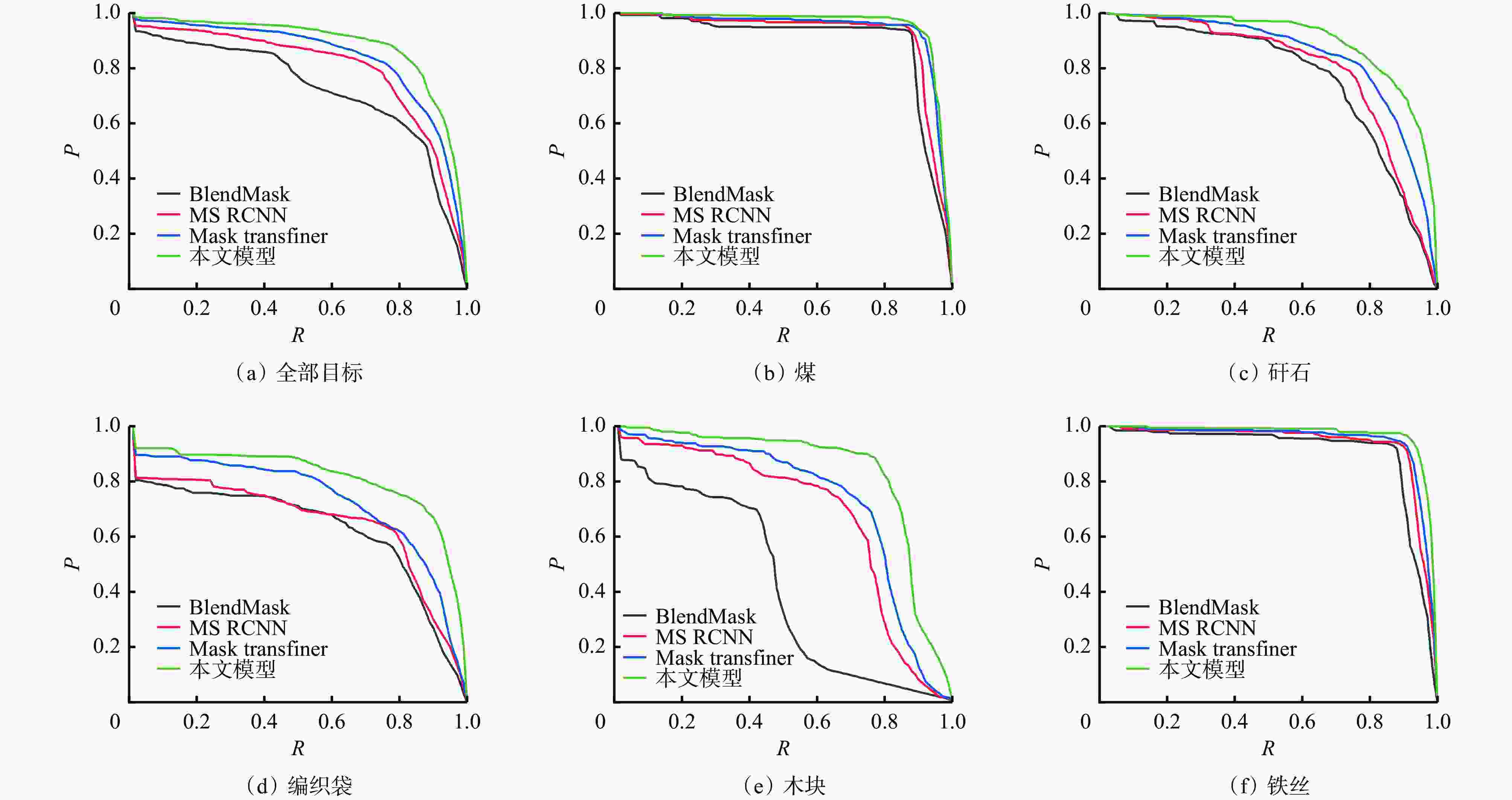
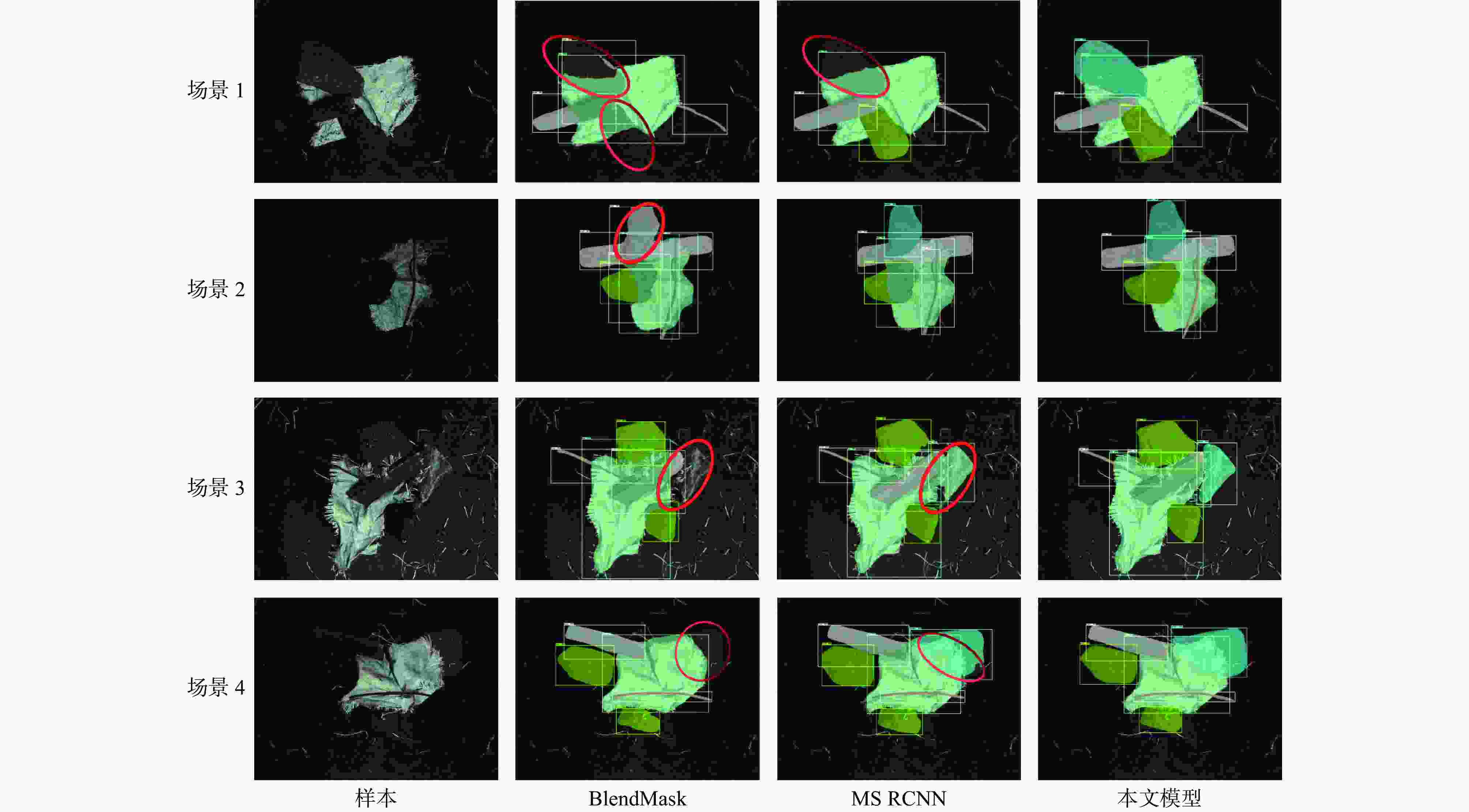
网络模型 输入 AP/% AP0.5/% AP0.75/% APS/% APM/% APL/% 单帧检测时间/ms SOLOv2 RGB 72.8 91.6 82.1 28.8 57.6 78.3 72.6 BlendMask RGB 67.1 87.5 78.5 26.8 48.7 72.6 60.7 Mask−RCNN RGB 70.6 91.0 79.1 27.7 54.1 76.2 102.6 MS RCNN RGB 73.5 91.8 83.2 29.9 58.5 79.1 126.4 Mask transfiner RGB 78.3 93.9 88.3 31.5 60.3 83.2 96.3 本文模型 RGB+Depth 82.2 96.8 93.7 33.1 62.5 86.6 110.5 -
[1] 刘峰,郭林峰,赵路正. 双碳背景下煤炭安全区间与绿色低碳技术路径[J]. 煤炭学报,2022,47(1):1-15.LIU Feng,GUO Linfeng,ZHAO Luzheng. Research on coal safety range and green low-carbon technology path under the dual-carbon background[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2022,47(1):1-15. [2] 刘峰,曹文君,张建明,等. 我国煤炭工业科技创新进展及“十四五”发展方向[J]. 煤炭学报,2021,46(1):1-15.LIU Feng,CAO Wenjun,ZHANG Jianming,et al. Current technological innovation and development direction of the 14(th) Five-Year Plan period in China coal industry[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2021,46(1):1-15. [3] 曹现刚,刘思颖,王鹏,等. 面向煤矸分拣机器人的煤矸识别定位系统研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2022,50(1):237-246. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2336.2022.1.mtkxjs202201024CAO Xiangang,LIU Siying,WANG Peng,et al. Research on coal gangue identification and positioning system based on coal-gangue sorting robot[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2022,50(1):237-246. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2336.2022.1.mtkxjs202201024 [4] LI Man,DUAN Yong,HE Xianli,et al. Image positioning and identification method and system for coal and gangue sorting robot[J]. International Journal of Coal Preparation and Utilization,2022,42(4/6):1759-1777. [5] 赵跃民,张亚东,周恩会,等. 清洁高效干法选煤研究进展与展望[J]. 中国矿业大学学报,2022,51(3):607-616. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1964.2022.3.zgkydxxb202203023ZHAO Yuemin,ZHANG Yadong,ZHOU Enhui,et al. Research progress and prospect of clean and efficient dry coal separation[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology,2022,51(3):607-616. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1964.2022.3.zgkydxxb202203023 [6] 葛世荣,郝尚清,张世洪,等. 我国智能化采煤技术现状及待突破关键技术[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2020,48(7):28-46.GE Shirong,HAO Shangqing,ZHANG Shihong,et al. Status of intelligent coal mining technology and potential key technologies in China[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2020,48(7):28-46. [7] WANG Yuanbin,WANG Yujing,DANG Langfei. Video detection of foreign objects on the surface of belt conveyor underground coal mine based on improved SSD[J]. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing,2023,14:5507-5516. doi: 10.1007/s12652-020-02495-w [8] 郝帅,张旭,马旭,等. 基于CBAM−YOLOv5的煤矿输送带异物检测[J]. 煤炭学报,2022,47(11):4147-4156.HAO Shuai,ZHANG Xu,MA Xu,et al. Foreign object detection in coal mine conveyor belt based on CBAM-YOLOv5[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2022,47(11):4147-4156. [9] ZHANG Kanghui,WANG Weidong,LYU Ziqi,et al. Computer vision detection of foreign objects in coal processing using attention CNN[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence,2021,102. DOI: 10.1016/j.engappai.2021.104242. [10] 任志玲,朱彦存. 改进CenterNet算法的煤矿皮带运输异物识别研究[J]. 控制工程,2023,30(4):703-711.REN Zhiling,ZHU Yancun. Research on foreign object detection of coal mine belt transportation with improved CenterNet algorithm[J]. Control Engineering of China,2023,30(4):703-711. [11] 程德强,徐进洋,寇旗旗,等. 融合残差信息轻量级网络的运煤皮带异物分类[J]. 煤炭学报,2022,47(3):1361-1369.CHENG Deqiang,XU Jinyang,KOU Qiqi,et al. Lightweight network based on residual information for foreign body classification on coal conveyor belt[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2022,47(3):1361-1369. [12] SONG Xinhang,JIANG Shuqiang,HERRANZ L,et al. Learning effective RGB-D representations for scene recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing,2019,28(2):980-993. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2018.2872629 [13] BALTRUŠAITIS T,AHUJA C,MORENCY L-P. Multimodal machine learning:a survey and taxonomy[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2019,41(2):423-443. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2798607 [14] GAO Mingliang,JIANG Jun,ZOU Guofeng,et al. RGB-D-based object recognition using multimodal convolutional neural networks:a survey[J]. IEEE Access,2019,7:43110-43136. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2907071 [15] LIN T-Y,DOLLAR P,GIRSHICK R B,et al. Feature pyramid networks for object detection[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,Honolulu,2017:936-944. [16] HE Kaiming,ZHANG Xiangyu,REN Shaoqing,et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,Las Vegas,2016:770-778. [17] MA Jiayi,MA Yong,LI Chang. Infrared and visible image fusion methods and applications:a survey[J]. Information Fusion,2019,45:153-178. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2018.02.004 [18] RAMACHANDRAM D,TAYLOR G W. Deep multimodal learning:a survey on recent advances and trends[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine,2017,34(6):96-108. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2017.2738401 [19] HOU Qibin,ZHOU Daquan,FENG Jiashi. Coordinate attention for efficient mobile network design[C]. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,Nashville,2021:13713-13722. [20] REN Shaoqing,HE Kaiming,GIRSHICK R,et al. Faster R-CNN:towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2017,39(6):1137-1149. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031 [21] WANG Xinlong,ZHANG Rufeng,KONG Tao,et al. SOLOv2:dynamic and fast instance segmentation[EB/OL]. [2023-09-12]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2003.10152. [22] CHEN Hao,SUN Kunyang,TIAN Zhi,et al. BlendMask:top-down meets bottom-up for instance segmentation[C]. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,Seattle,2020:8570-8578. [23] HE Kaiming,GKIOXARI G,DOLLÁR P,et al. Mask R-CNN[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence,2017,42(2):2980-2988. [24] HUANG Zhaojin,HUANG Lichao,GONG Yongchao,et al. Mask scoring R-CNN[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,Washington,2019:6409-6418. [25] KE Lei,DANELLJAN M,LI Xia,et al. Mask transfiner for high-quality instance segmentation[C]. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,New Orleans,2022:4402-4411. -



 下载:
下载: