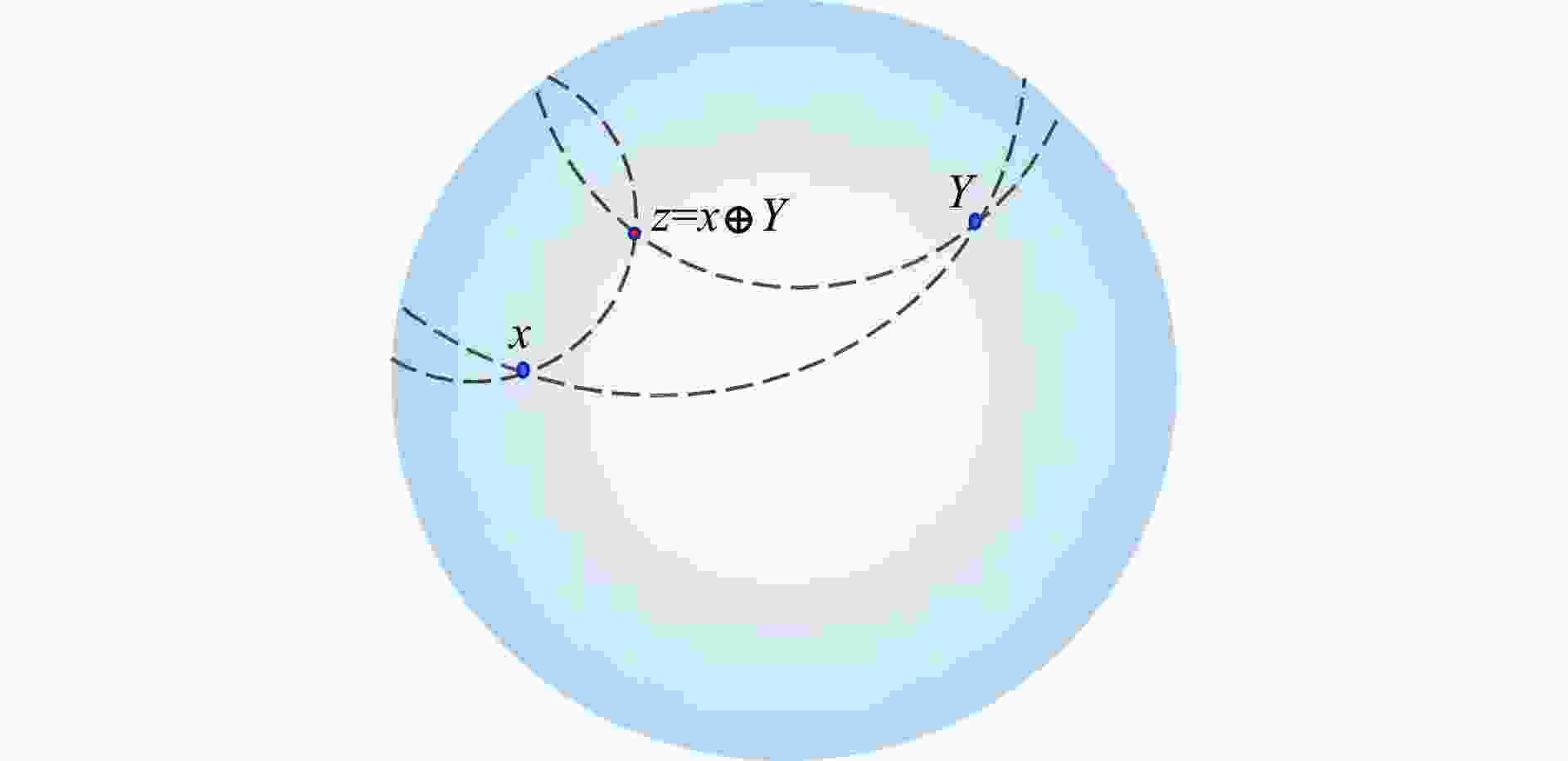
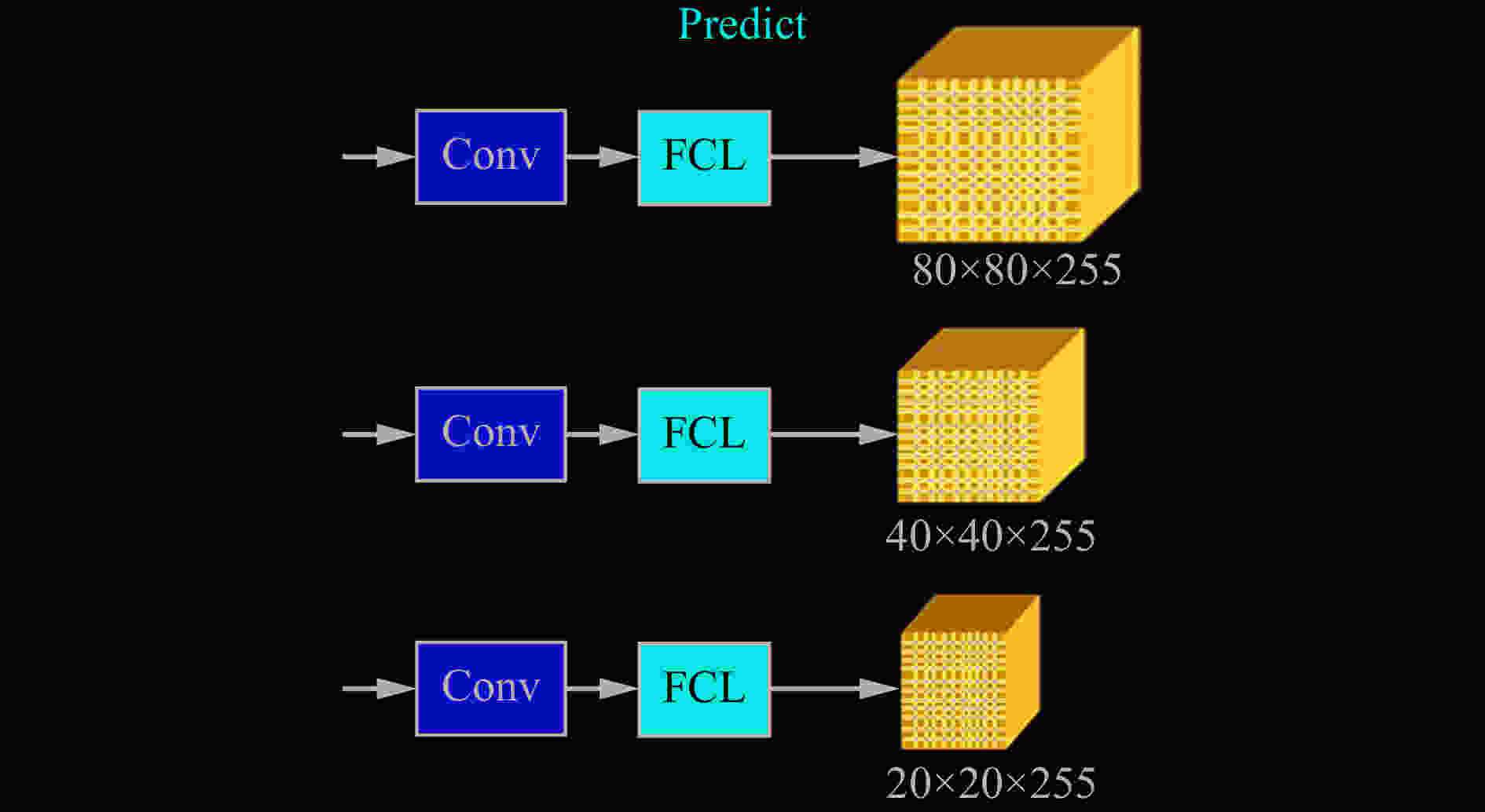
A multi-target road detection model in a low-light environment in an open-pit mining area based on hyperbolic embedding
-
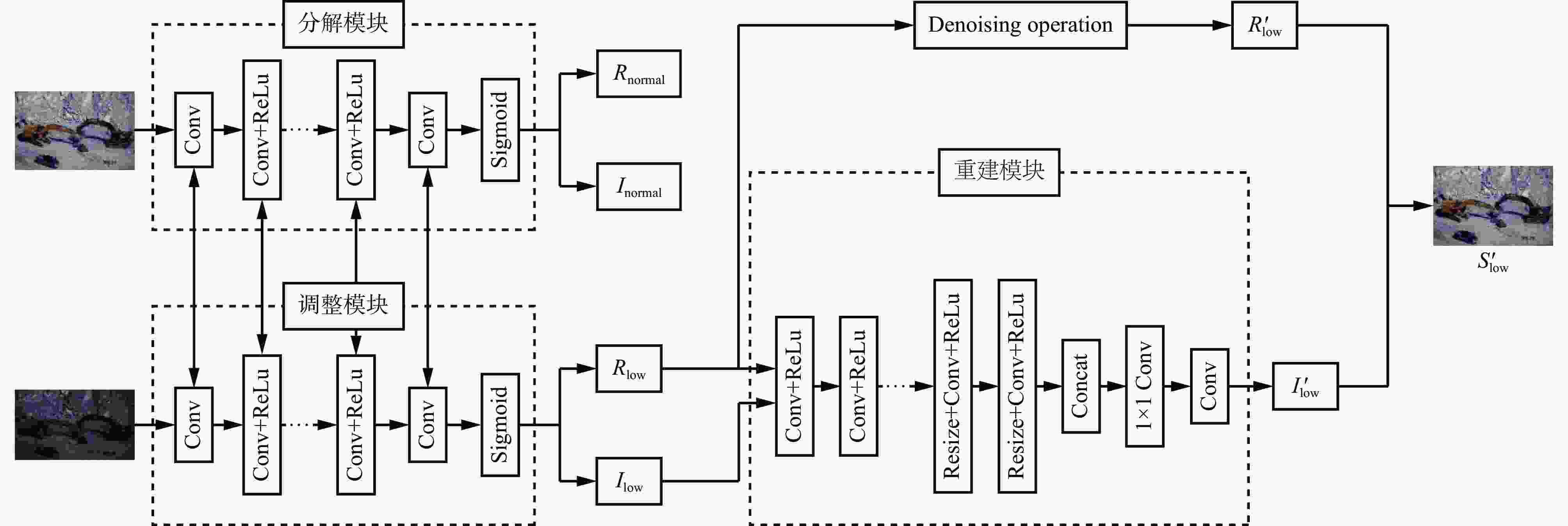
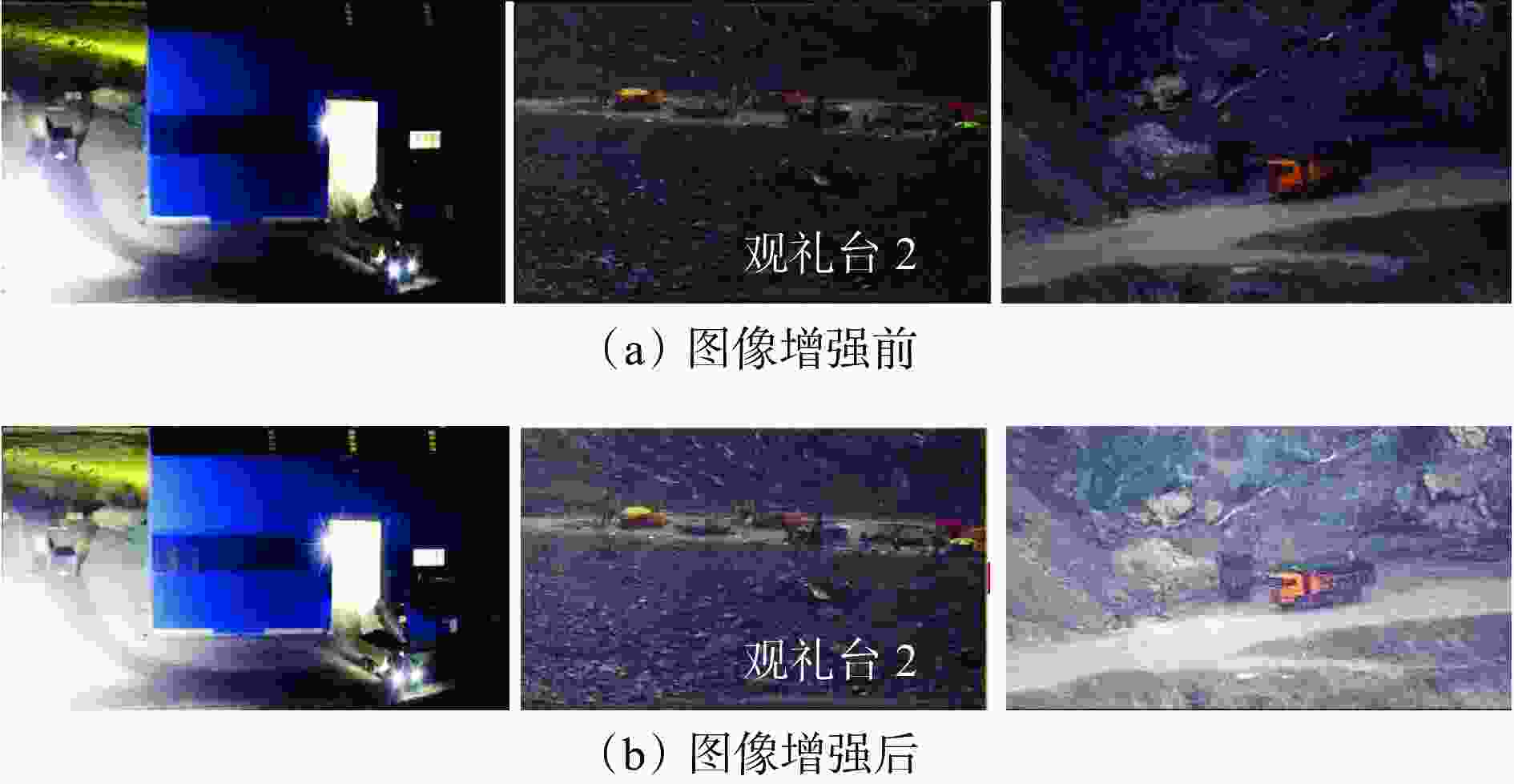
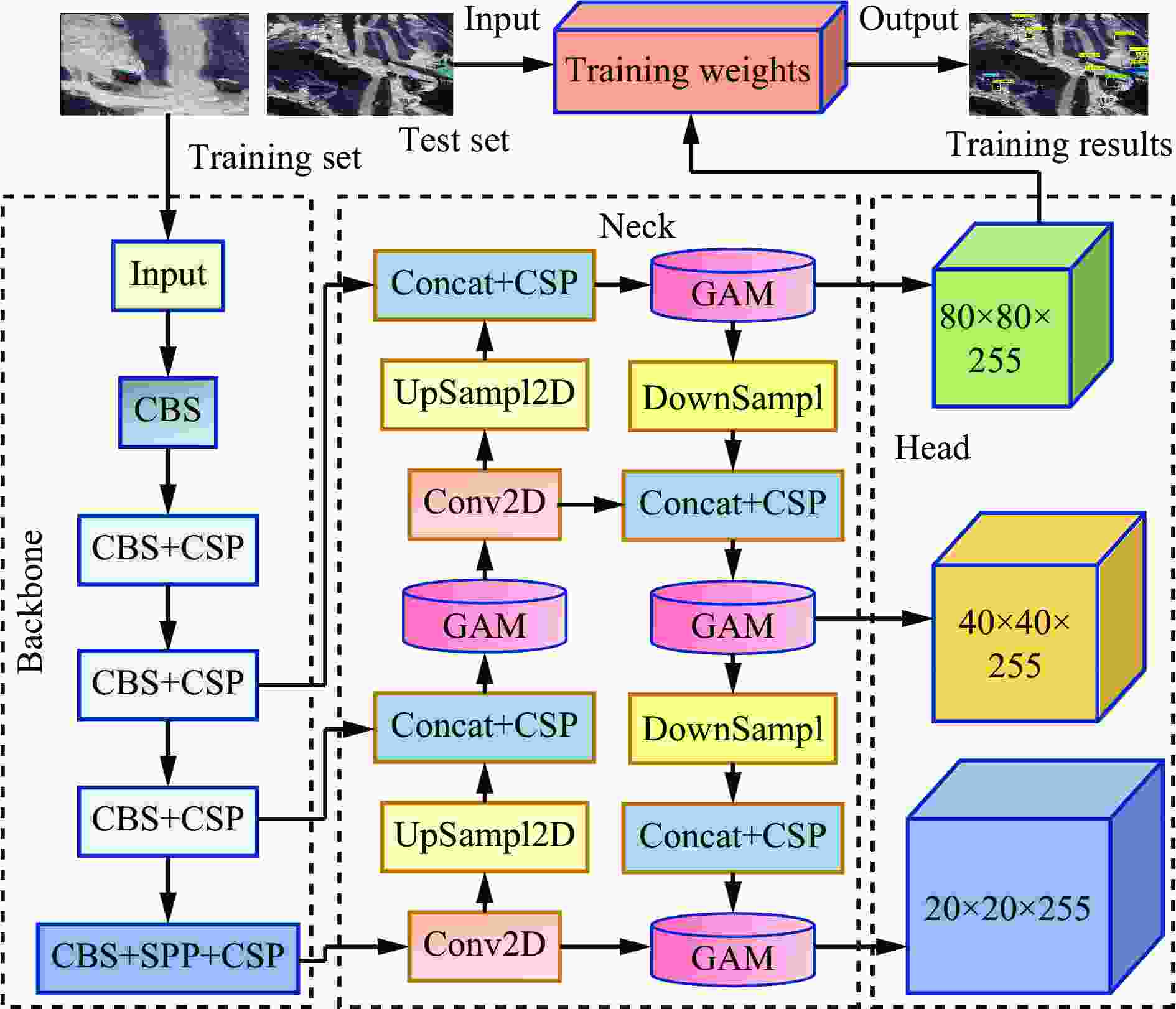
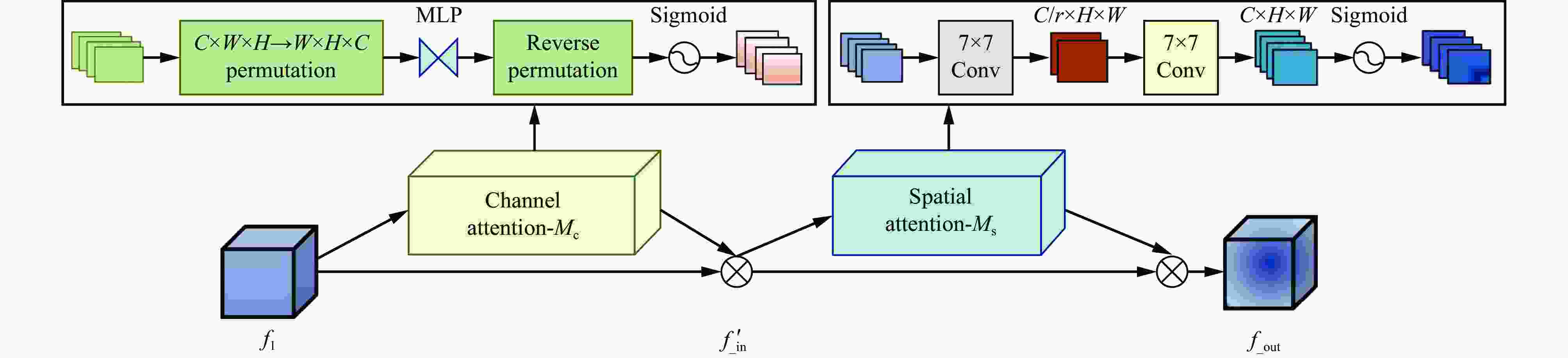
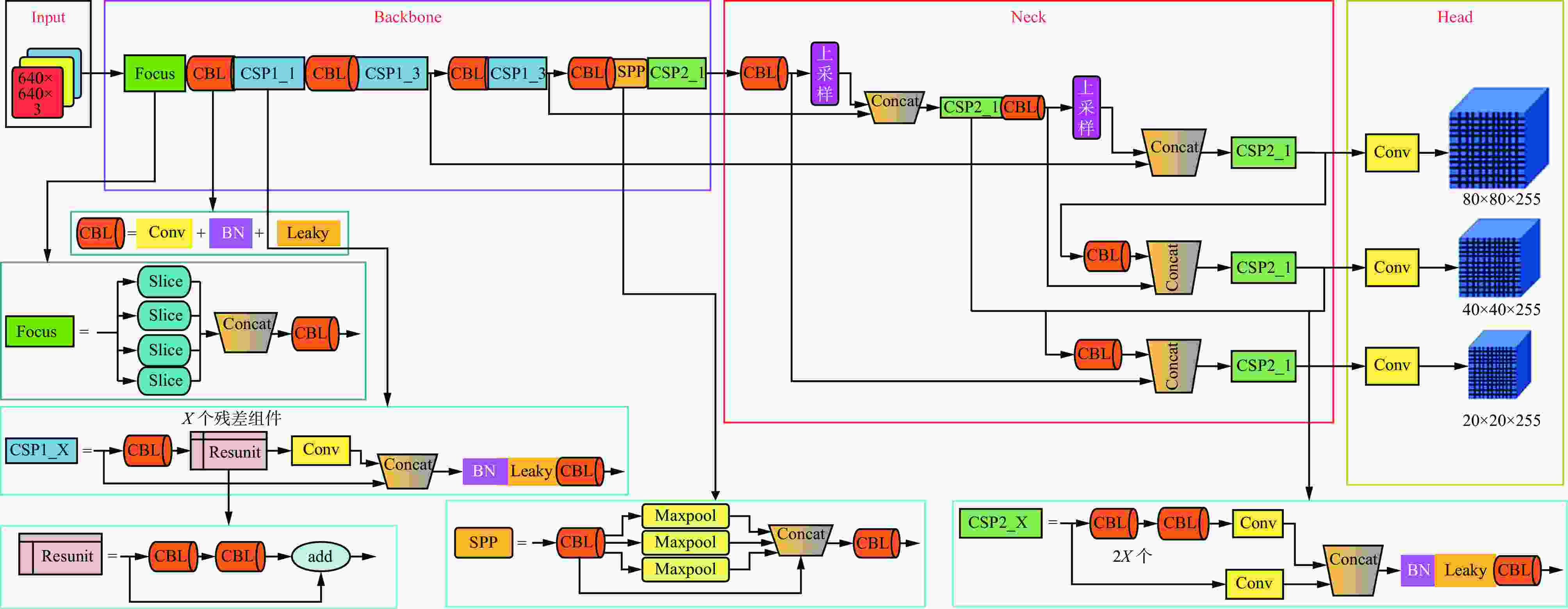
摘要: 露天矿环境特殊,道路场景复杂多变,在光照不足时会导致矿区道路多目标识别不清、定位不准,进而影响检测效果,给矿区无人矿用卡车的安全行驶带来严重安全隐患。目前的道路障碍物检测模型不能有效解决矿区暗光环境对模型检测效果的影响,同时对矿区小目标障碍物的识别也有较大误差,不适用于矿区特殊环境下障碍物的检测与识别。针对上述问题,提出了一种基于双曲嵌入的露天矿区暗光环境下多目标检测模型。首先,在模型的图像预处理阶段引入卷积神经网路Retinex−Net对暗图像进行增强,提高图像清晰度;然后,针对数据集中特征过多而无重点偏好的问题,在加强特征提取部分添加全局注意力机制,聚集3个维度上更关键的特征信息;最后,在检测模型预测阶段引入双曲全连接层,以减少特征丢失,并防止过拟合现象。实验结果表明:① 基于双曲嵌入的露天矿区暗光环境下道路多目标检测模型不仅对露天矿区暗光环境下的大尺度目标具有较高的分类与定位精度,对矿用卡车及较远距离的小尺度目标即行人也可准确检测与定位,能够满足无人矿用卡车在矿区特殊环境下驾驶的安全需求。② 模型的检测准确率达98.6%,检测速度为51.52 帧/s,较SSD、YOLOv4、YOLOv5、YOLOx、YOLOv7分别提高20.31%,18.51%,10.53%,8.39%,13.24%,对于矿区道路上的行人、矿用卡车及挖机的检测精度达97%以上。Abstract: The environment of open-pit mines is distinctive, and the conditions of the roads in them are complex and constantly changing. Insufficient lighting in the area being mined can make it challenging to identify and position multiple targets on the roads. This, in turn, affects the results of detection and poses serious risks to the safe operation of uncrewed mining trucks.Currently available models to identify obstacles on roads cannot accommodate the impact of poor lighting, and thus, yield inaccurate results. They also have significant shortcomings in identifying small obstacles in the mining area. In this study, we develop a multi-target model of detection for the dark/light environment of an open-pit mine using hyperbolic embedding to address the above-mentioned issues. We introduce the Retinex-Net convolutional neural network to the image preprocessing stage of the detection model to enhance dark images and improve their clarity. To address the issue of an excessively large number of features in the dataset without a clear preference for focus, we incorporate the global attention mechanism into the improved process of feature extraction. This enabled the collection of critical feature-related information in three dimensions. Finally, we incorporate a fully connected hyperbolic layer into the prediction stage of the model to minimize feature loss and prevent overfitting. The results of experiments to verify the proposed model showed that ① it could reliably classify and accurately identify large-scale targets in the low-light environment of the open-pit mining area, and was able to highly accurately identify mining trucks and small vehicles over long distances. It could also accurately identify and locate scaled targets, including pedestrians, such that this satisfies meeting the safety-related requirements of uncrewed mining trucks operating in diverse environments.② The model achieved an accuracy of detection of 98.6% while maintaining a speed of 51.52 frames/s, where this was 20.31%, 18.51%, 10.53%, 8.39%, and 13.24% higher than the accuracies of the SSD, YOLOv4, YOLOv5, YOLOx, and YOLOv7, respectively. Its accuracy of detection of pedestrians, mining trucks, and excavators on mining roads exceeded 97%.
-
表 1 实验平台软硬件配置
Table 1. Hardware and software configuration of experimental platform
配置名称 型号/版本 GPU NVIDIA GeForce 3090(24 G) CPU Intel® Core™ i7−7800X CPU 操作系统 Windows 10 专业版 学习框架 Pytorch1.7.1, Python3.9, Cuda11.0 表 2 混淆矩阵评价
Table 2. Confusion matrix evolution
混淆矩阵 真实值 正样本 负样本 预测值 正样本 真正样本数(NTP) 假负样本数(NFP) 负样本 假正样本数(NFN) 真负样本数(NTN) 表 3 混淆矩阵性能指标计算公式
Table 3. Calculation formula of performance indexs of confusion matrix
指标 公式 精确率(P) $ \dfrac{{{N_{\rm{{TP}}}}}}{{{N_{\rm{{TP}}}} + {N_{\rm{{FP}}}}}} $ 召回率(Q) $ \dfrac{{{N_{\rm{{TP}}}}}}{{{N_{\rm{{TP}}}} + {N_{\rm{{FN}}}}}} $ 平均精度 $ \dfrac{{\displaystyle\sum\limits_1^B {PQ} }}{B} $ 准确率 $ \dfrac{{{N_{\rm{{TP}}}} + {N_{\rm{{TN}}}}}}{{{N_{\rm{{TP}}}} + {N_{\rm{{TN}}}} + {N_{\rm{{FP}}}} + {N_{\rm{{FN}}}}}} $ F1度量 $ \dfrac{{2PQ}}{{P + Q}} $ 表 4 消融实验结果
Table 4. Ablation test results
Retinex−Net GAM 双曲全连接层 检测速度/(帧·s−1) 准确率/% × × × 53.44 79.30 √ × × 54.31 83.30 × √ × 53.19 87.53 × × √ 52.02 93.81 √ √ √ 51.52 98.60 表 5 不同网络性能对比
Table 5. Performance comparison of different networks
模型 输入尺寸 准确
率/%检测速度/
(帧·s−1)平均检测精度/% 行人 矿卡 挖机 SSD 640×640 78.36 104.96 69.11 83.37 89.35 YOLO v4 640×640 80.16 63.97 83.94 78.03 91.93 YOLOv5 640×640 88.14 51.44 93.13 92.80 93.69 YOLOx 640×640 90.28 54.21 94.88 90.89 94.53 YOLOv7 640×640 85.43 49.38 95.81 96.33 95.93 本文模型 640×640 98.67 55.25 97.61 97.03 98.23 -
[1] ZHANG Shifeng,WEN Longyin,BIAN Xiao,et al. Occlusion-aware R-CNN:detecting pedestrians in a crowd[C]. European Conference on Computer Vision,Munich,2018. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-01219-9_39. [2] LI Jianan,LIANG Shengmei,XU Tingfa,et al. Scale-aware fast R-CNN for pedestrian dettion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia,2018,20(4):985-996. [3] CHENG Bowen,WEI Yunchao,SHI Honghui,et al. Revisiting R-CNN:on awakening the classification power of faster R-CNN[C]. European Conference on Computer Vision,Munich,2018:8-14. [4] 秦振,李学伟,刘宏哲. 基于改进SSD的鲁棒小目标检测算法[J]. 东北师大学报(自然科学版),2023,55(4):59-66.QIN Zhen,LI Xuewei,LIU Hongzhe. Robust small target detection algorithm based on improved SSD[J]. Journal of Northeast Normal University(Natural Science Edition),2023,55(4):59-66. [5] FU Chengyang,LIU Wei,RANGA A,et al. DSSD:deconvolutional single shot detector[Z/OL]. arXiv,2017. https://arxiv.org/abs/1701.06659. [6] LI Z X,ZHOU Fuqiang. FSSD:feature fusion single shot multibox detector[Z/OL]. arXiv E-Prints,2017. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1712.00960. [7] REDMON J,DIVVALA S,GIRSHICK R,et al. You only look once:unified,real-time object detection[C]. IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision,Los Alamitos,2016:779-788. [8] REDMON J,FARHADI A. Yolo9000:better,faster,stronger[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,Honolulu,2017:6517-6525. [9] REDMON J,FARHADI A. Yolov3:an incremental improvment[Z/OL]. arXiv E-Prints,2018. https://arxiv.org/abs/1804.02767. [10] BOCHKOVSKIY A,WANG C Y,LIAO H Y M. Yolov4:optimal speed and accuracy of object detection[Z/OL]. arXiv E-Prints,2020. https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.10934. [11] YAN Mingyang,SUN Jianbo. A dim-small target real-time detection method based on enhanced YOLO[C]. IEEE International Conference on Electrical Engineering,Big Data and Algorithms,Changchun,2022:567-571. [12] LIU Wei,ANGUELOV D,ERHAN D,et al. SSD:single shot multibox detector[C]. European Conference on Computer Vision,Cham,2016:21-37. [13] ZHANG Sheng,WANG Xu,LI Ping,et al. An improved YOLO algorithm for rotated object detection in remote sensing images [C]. IEEE 4 th Advance Information Management,Communicates,Electronic and Automation Control Conference,Chongqing,2021:840-845. [14] MATTHIES L,RANKIN A. Negative obstacle detection by thermal signature[C]. IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems,Las Vegas,2003. DOI: 10.1109/IROS.2003.1250744. [15] SVENNINGSSON P,FIORANELLI F,YAROVOY A. Radar-pointGNN:graph based object recognition for unstructured radar point-cloud data[C]. IEEE Radar Conference,Atlanta,2021. DOI: 10.1109/RadarConf2147009.2021.9455172. [16] KUMAR R,JAYASHANKAR S. Radar and camera sensor fusion with ROS for autonomous driving[C]. 2019 Fifth International Conference on Image Information Processing,Shimla,2019:568-573. [17] JIN Yi,KUANG Yongshao,HOFFMANN M,et al. Radar and lidar deep fusion:providing doppler contexts to time-of-flight lidar[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal,2023,23(20):25587-25600. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2023.3313093 [18] BORJI A,ITTI L. State-of-the-art in visual attention modeling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2013,35(1):185-207. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2012.89 [19] KUANG Hulin,ZHANG Xianshi,LI Yongjie,et al. Nighttime vehicle detection based on bio-inspired image enhancement and weighted score-level feature fusion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems,2017,18:927-936. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2016.2598192 [20] KAEWTRAKULPONG P,BOWDEN R. An improved adaptive background mixture model for real-time tracking with shadow detection[C]. Processing of European Workshop Advanced Video Based Surveillance Systems,2002. DOI: 10.1007/978-1-4615-0913-4_11. [21] WANG C Y,LIAO H Y,YEH I H,et al. CSPNet:a new backbone that can enhance learning capability of CNN[C]. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops,Seattle,2020:1571-1580. [22] HE Kaiming,ZHANG Xiangyu,REN Shaoping,et al. Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence,2015,37(9):1904-1916. [23] LIN T Y,DOLLAR P,GIRSHICK R,et al. Feature pyramid networks for object detection[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,Honolulu,2017:936-944. [24] HU Jianfang,SUN Jiangxin,LIN Zihang,et al. APANet:auto-path aggregation for future instance segmentation prediction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2022,44(7):3386-3403. [25] WEI Chen,WANG Wenjing,YANG Wenhan,et al. Deep retinex decomposition for low-light enhancement[J]. arXiv E-Prints,2018. DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.1808.04560. [26] 李正龙,王宏伟,曹文艳,等. 基于含噪Retinex模型的煤矿低光照图像增强方法[J]. 工矿自动化,2023,49(4):70-77.LI Zhenglong,WANG Hongwei,CAO Wenyan,et al. A method for enhancing low light images in coal mines based on Retinex model containing noise[J]. Journal of Mine Automation,2023,49(4):70-77. [27] LIU Yichao,SHAO Zongru,HOFFMANN N. Global attention mechanism:retain information to enhance channel-spatial interactions[J]. arXiv E-Prints,2021. DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.2112.05561. [28] LIN H,TEGMARK M,TEGMARK M E. Critical behavior in physics and probabilistic formal languages[J]. Entropy,2019,19(7):299. [29] KATAYAMA K,MAINA E W. Indexing method for hierarchical graphs based on relation among interlacing sequences of eigenvalues[J]. Ipsj Journal,2015,56(2):210-220. [30] BRONSTEIN M M,BRUNA J,LECUN Y,et al. Geometric deep learning:going beyond euclidean data[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine,2017. DOI: 10.1109/msp.2017.2693418. -
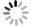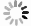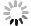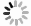



 下载:
下载: