Prediction model of coal spontaneous combustion temperature based on data filling
-
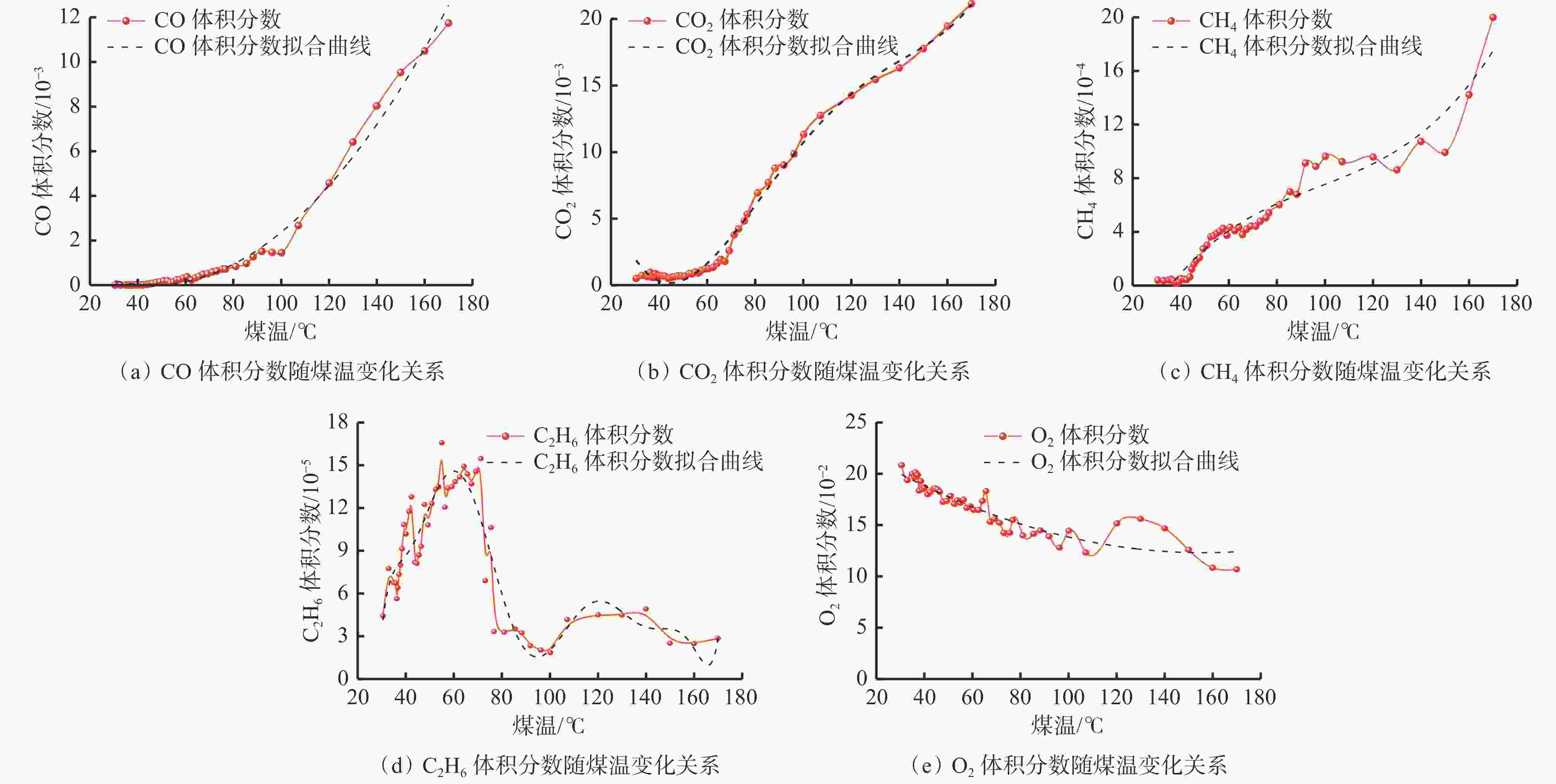
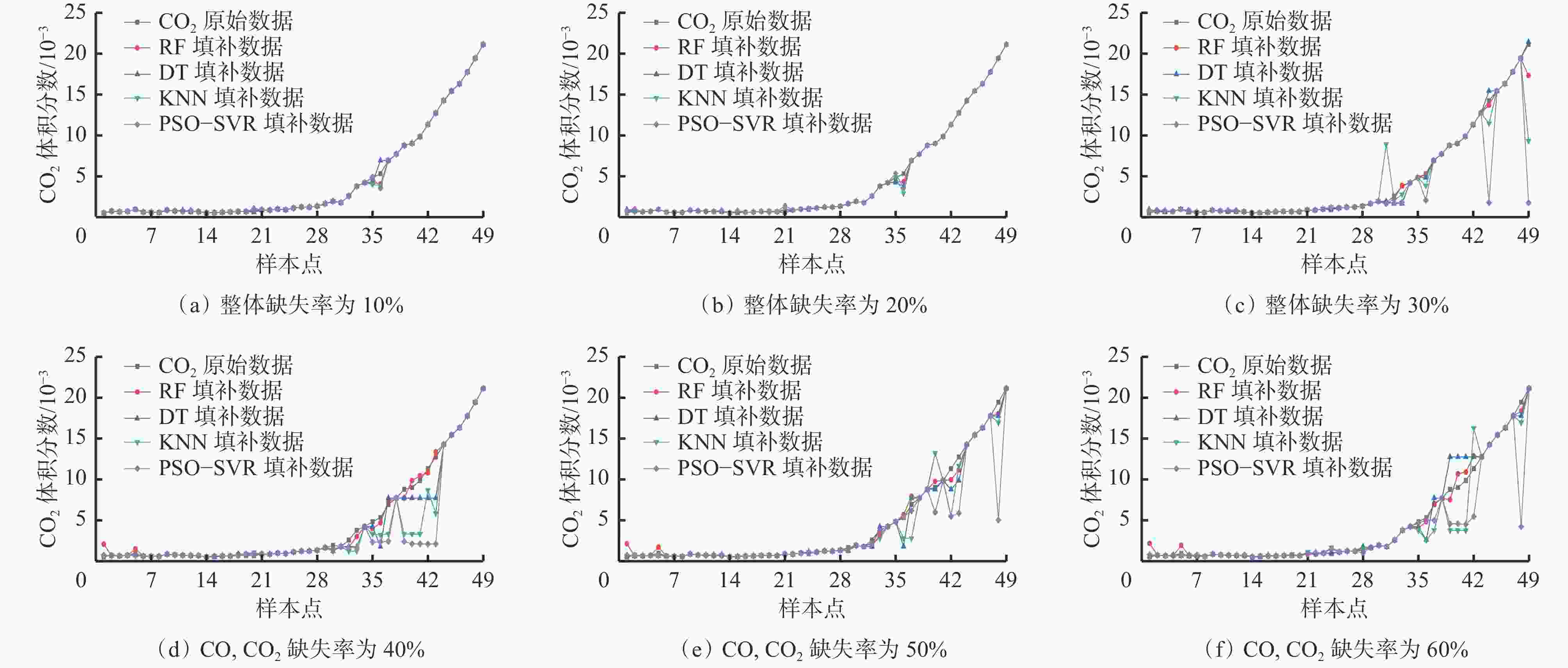
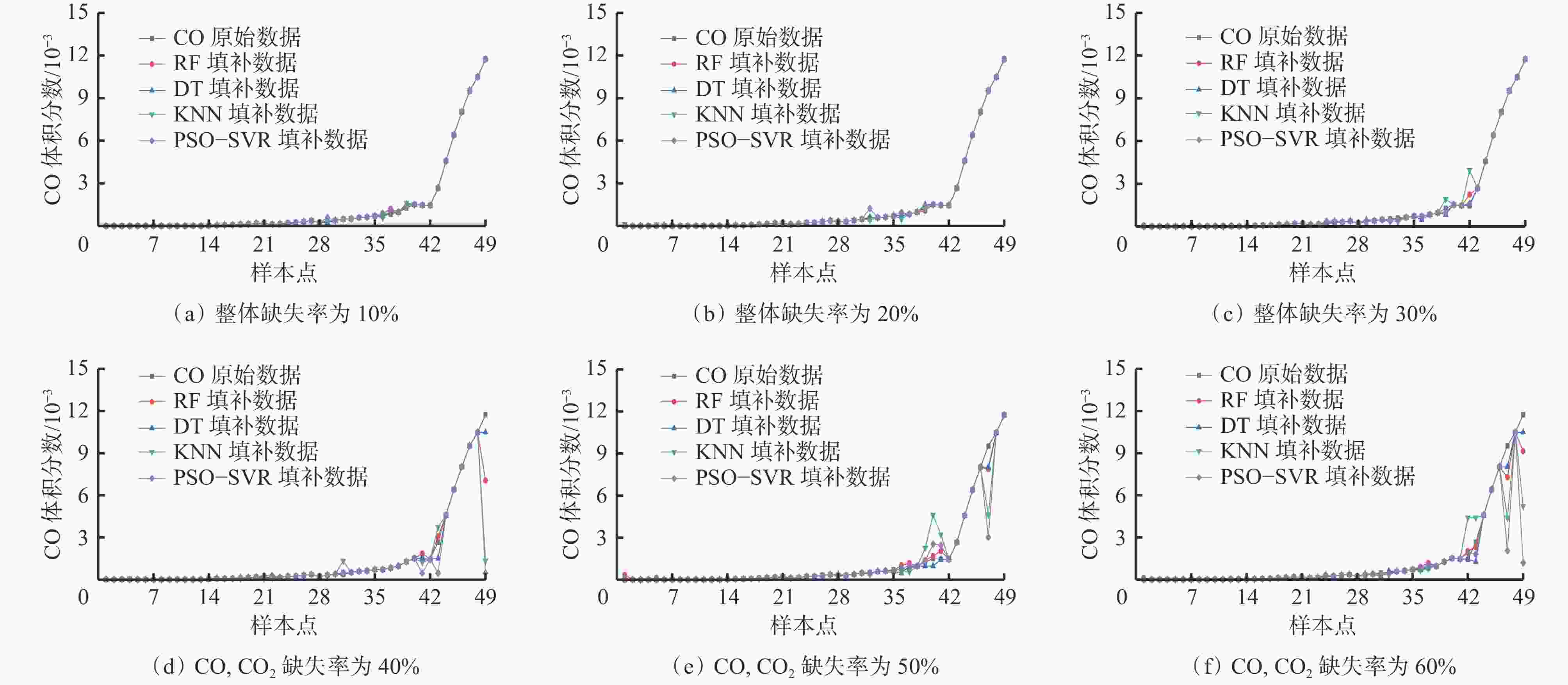
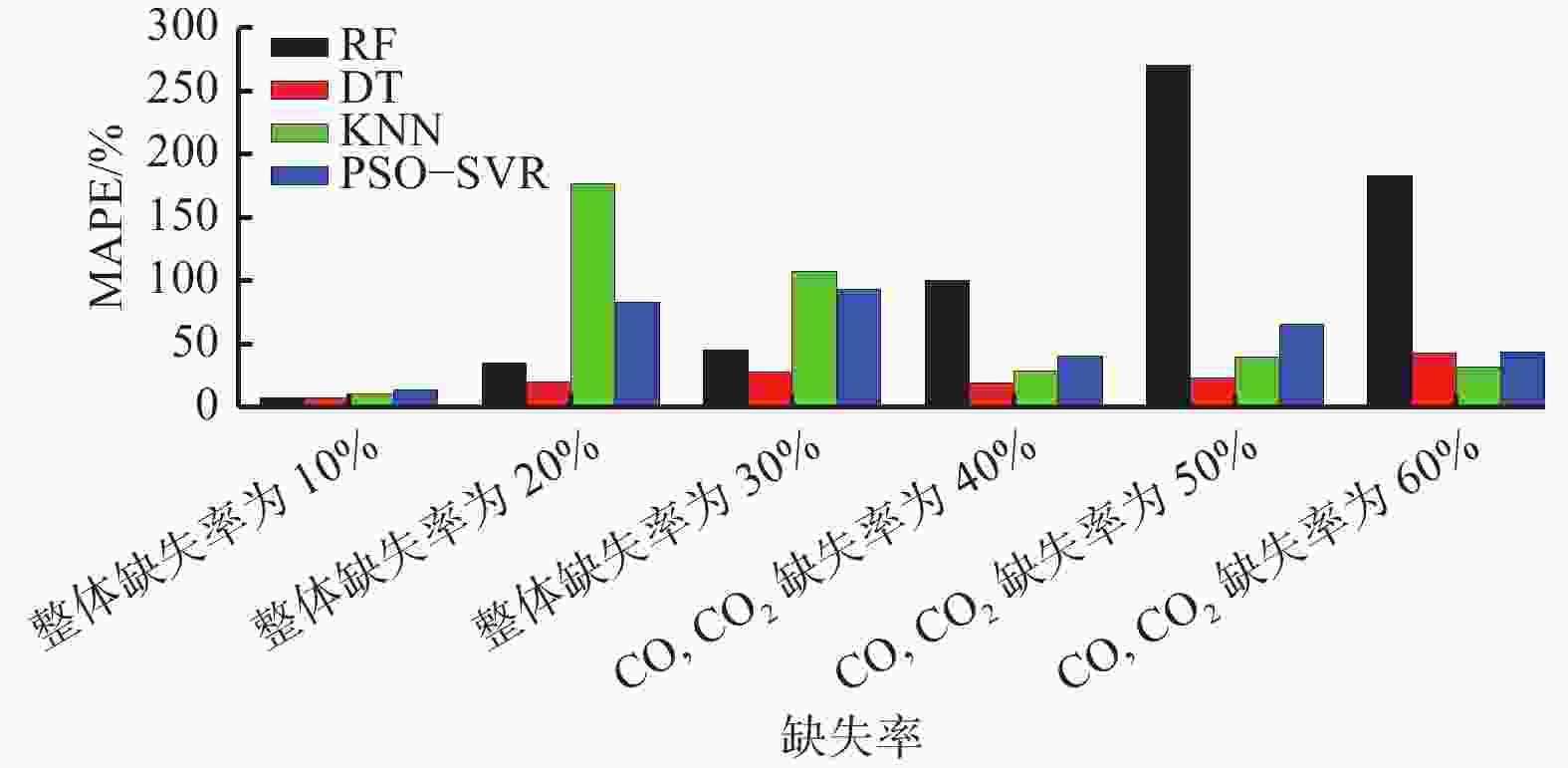
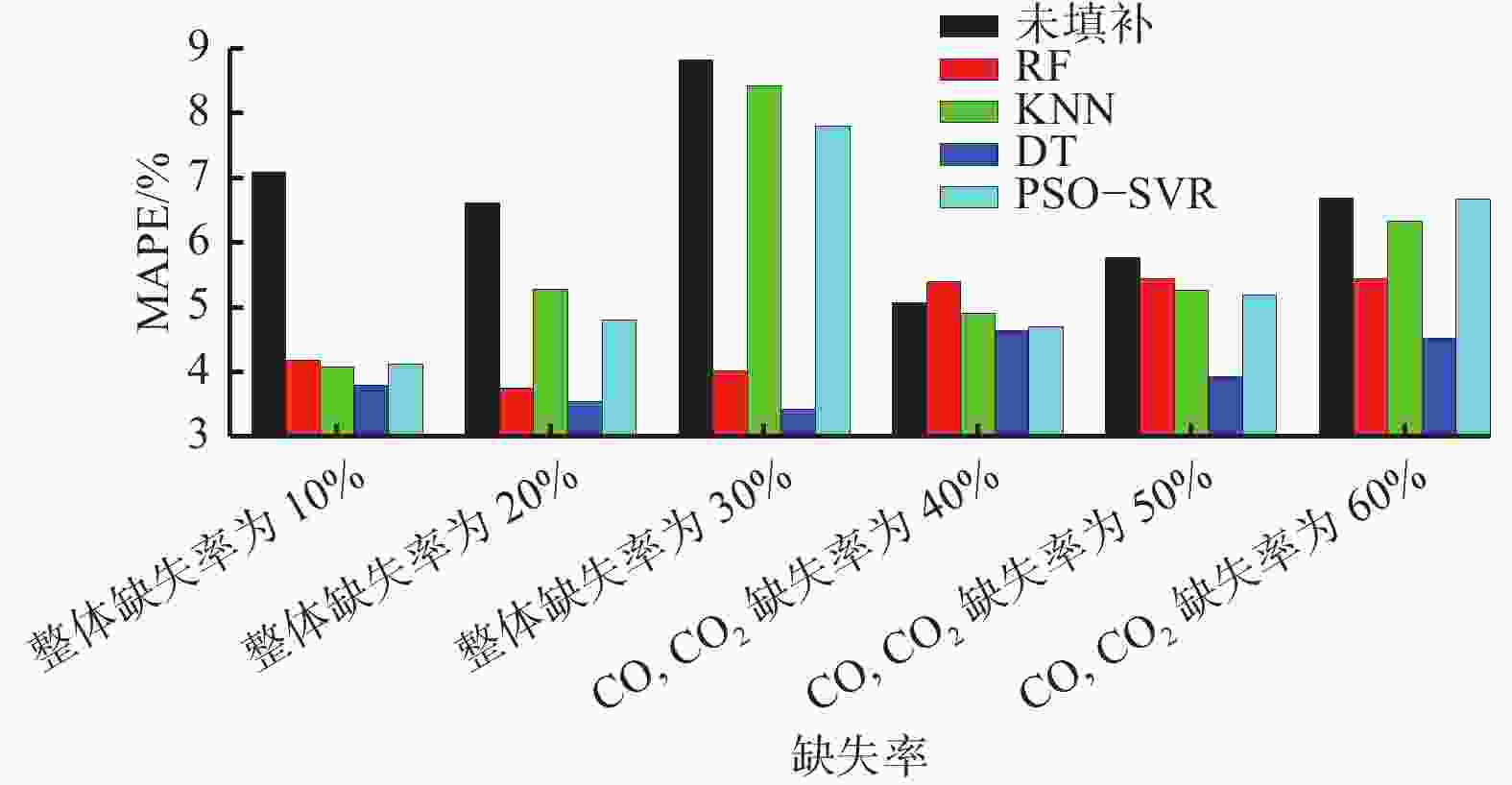
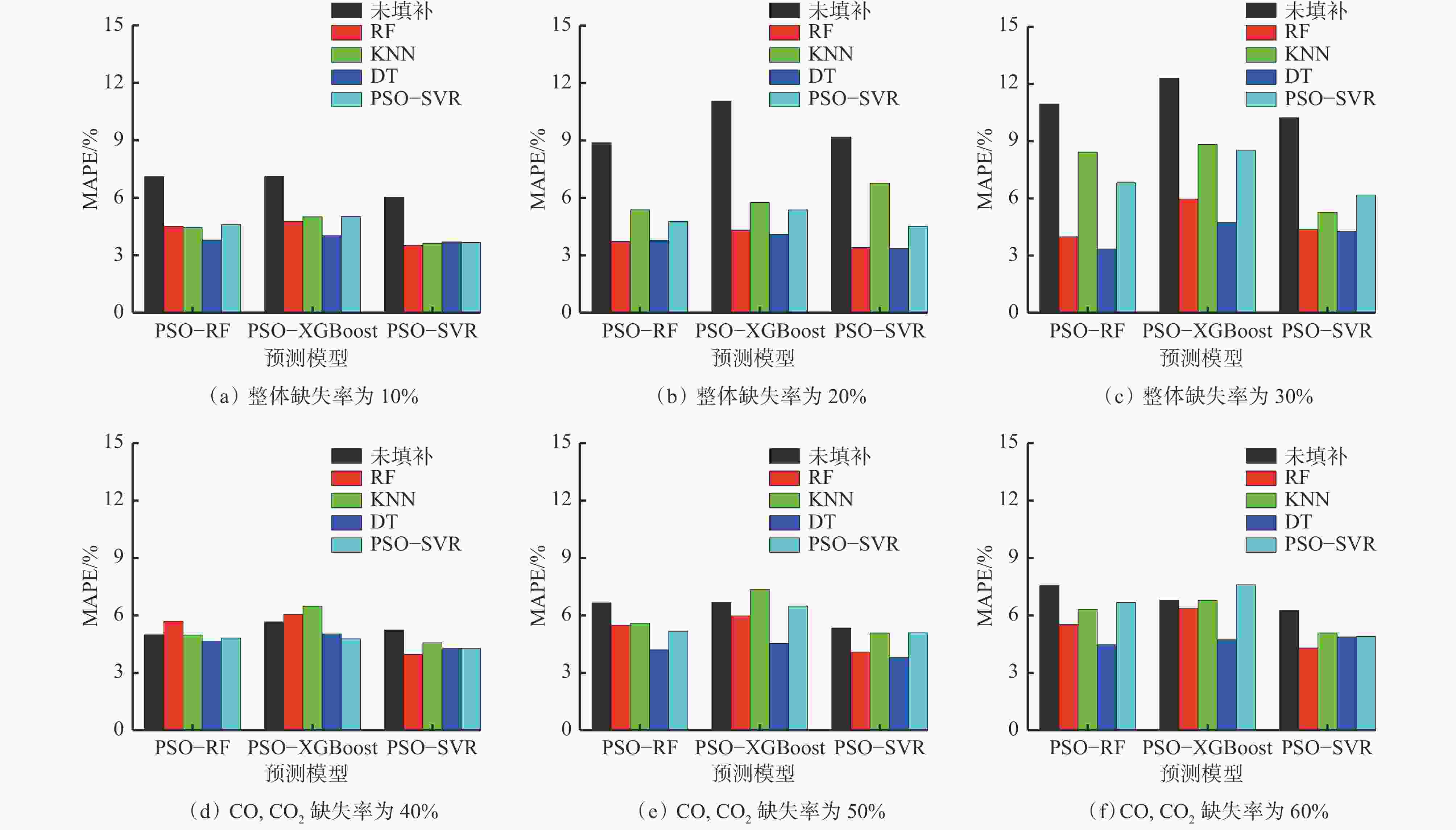
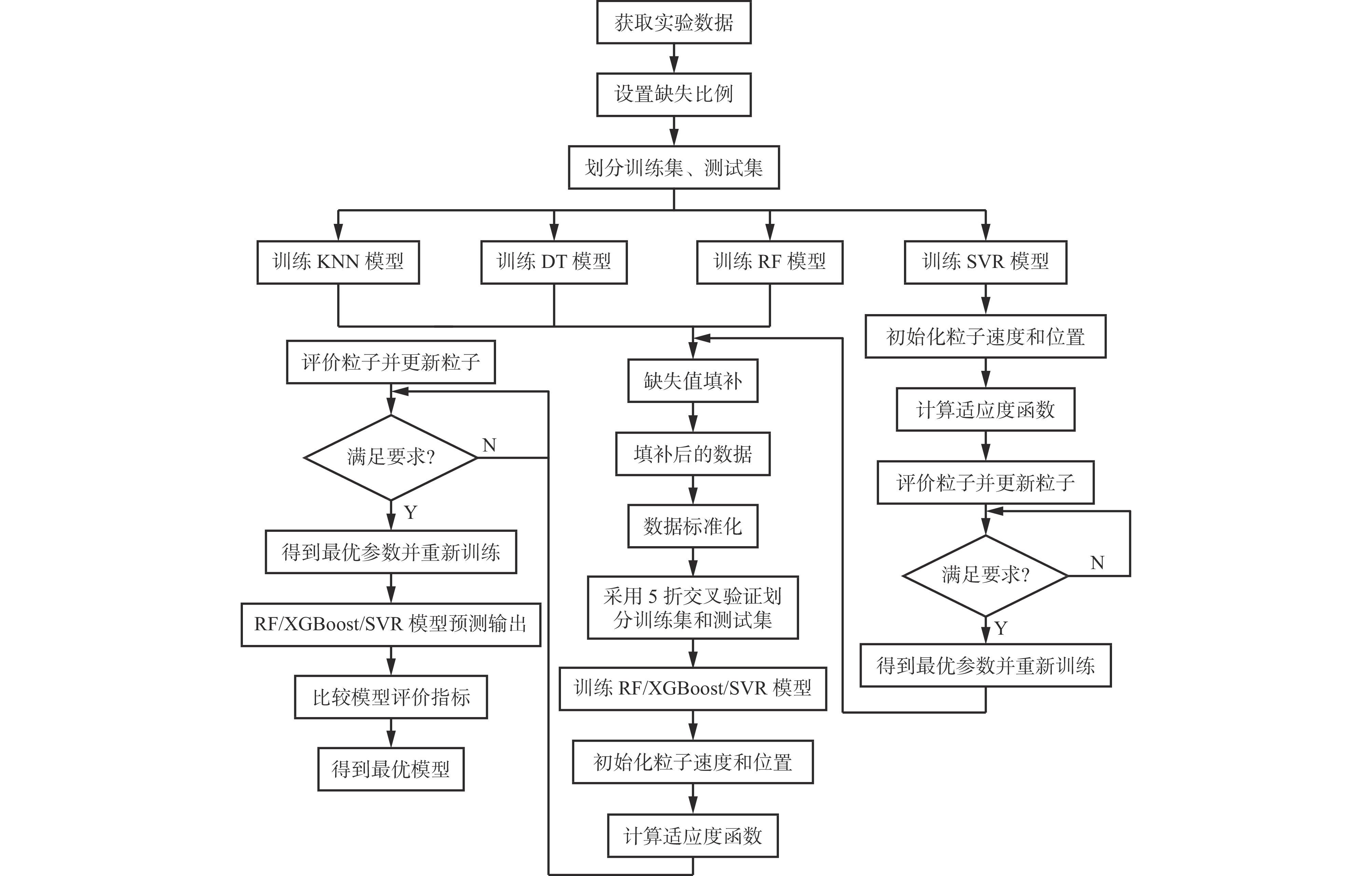
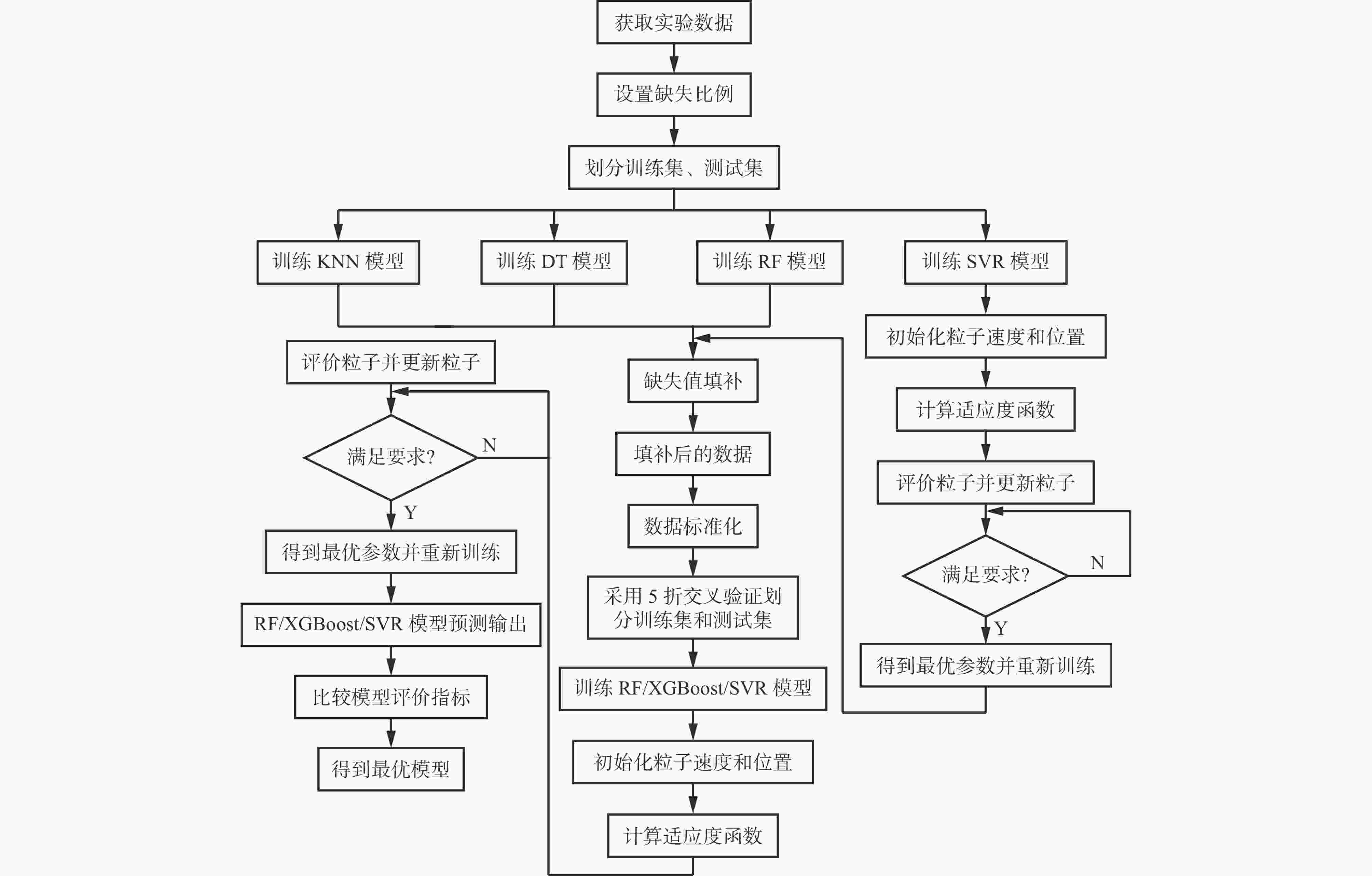
摘要: 现有煤自燃温度预测模型的建立大多基于较为完整的指标气体样本数据,但指标气体数据受仪器或人为因素影响,往往存在数据缺失现象,导致煤自燃温度预测准确率较低和过拟合等问题。针对上述问题,提出了将K近邻算法(KNN)、随机森林(RF)、决策树(DT)及基于粒子群优化的支持向量回归等填补算法(PSO−SVR)应用于缺失值填补,缺失数据和填补后的数据通过RF、SVR和极限梯度提升树(XGBoost)算法分别进行训练,并通过PSO算法优化参数,构建了基于数据填补的RF、XGBoost和SVR煤自燃温度预测模型。利用煤自然发火实验选取CO,CO2,CH4,C2H6,O2作为指标气体,并设计整体缺失率为10%,20%,30%和CO,CO2缺失率为40%,50%,60%共6种随机数据缺失,采用平均绝对误差百分比(MAPE)作为填补效果评价指标,采用MAPE、判断系数R2和均方根误差(RMSE)作为模型性能评价指标,对4种填补算法和3种预测模型进行对比。对比分析结果表明:在6种数据缺失情况下,DT填补算法填补效果优于其他3种算法,在CO,CO2存在较多缺失值时,RF算法的填补值与实际值的MAPE偏大;在不调参的情况下,XGBoost模型虽然在训练集效果极好,但极易过拟合,而SVR模型预测效果极差,无法满足预测要求;在6种数据缺失情况下,基于DT填补算法的PSO−SVR、RF与PSO−RF煤自燃温度预测模型的MAPE均在4%左右,基于DT填补算法的RF模型无需优化就能较好地预测出煤自燃温度,具有良好的稳定性。Abstract: Most of the existing coal spontaneous combustion temperature prediction models are based on relatively complete index gas sample data. However, the index gas data are affected by instruments or human factors. There are often data missing phenomena, resulting in low accuracy and over-fitting of coal spontaneous combustion temperature prediction. In order to solve the above problems, the paper proposes to apply filling algorithms such as K-nearest neighbor algorithm (KNN), random forest algorithm (RF), decision tree algorithm (DT) and support vector regression algorithm based on particle swarm optimization (PSO-SVR) to fill in the missing values. The missing data and the filled data are trained by RF, SVR and extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost) algorithm respectively. The parameters are optimized by the PSO algorithm. The RF, XGBoost and SVR coal spontaneous combustion temperature prediction models based on data filling are constructed. CO, CO2, CH4, C2H6 and O2 are selected as index gas in coal spontaneous combustion experiment, and six kinds of random data missing are designed. The overall missing rates are designed as 10%, 20% and 30%. The missing rates of CO and CO2 are designed as 40%, 50% and 60%. The average absolute error percentage (MAPE) is used as the filling effect evaluation index. The MAPE, the judgment coefficient R2 and the root mean square error (RMSE) are used as the model performance evaluation index. Four filling algorithms and three prediction models are compared. The results of the comparative analysis show the following points. The DT filling algorithm has better filling effect than the other three algorithms in six kinds of missing data cases. When there are more missing values of CO and CO2, the MAPE between the filling value and the actual values of the RF algorithm is large. The XGBoost model works extremely well in the training set without adjusting the parameters, but it is very prone to overfitting. The prediction effect of SVR model is very poor and the model cannot meet the prediction requirements. In the case of six kinds of data missing, the MAPE of PSO-SVR, RF and PSO-RF coal spontaneous combustion temperature prediction models based on the DT filling algorithm are about 4%. The RF model based on the DT filling algorithm can predict the coal spontaneous combustion temperature without optimization and has good stability.
-
表 1 特征重要性
Table 1. Importance of characteristics
特征 CO CO2 CH4 C2H6 O2 特征重要性 0.259 0.427 0.186 0.028 0.101 表 2 基于完整数据的模型评价指标对比
Table 2. Comparison of model evaluation index based on complete data
预测
模型模型评价指标 训练集/测试集
RMSE/℃训练集/测试集
MAPE/%训练集/测试集
R2RF 1.856 /4.460 1.539 /4.034 0.997/0.978 XGBoost 0.001/4.544 0.001/4.650 1.000/0.975 SVR 30.782/30.994 24.678/30.190 0.198/0.198 表 3 基于完整数据的PSO优化后的模型指标对比
Table 3. Comparison of PSO optimized model index based on complete data
预测
模型模型评价指标 训练集/测试集
RMSE/℃训练集/测试集
MAPE/%训练集/测试集
R2PSO−RF 1.847/4.211 1.715/4.344 0.997/0.976 PSO−XGBoost 1.235/4.400 0.414/3.912 0.999/0.979 PSO−SVR 2.323/2.427 2.910/3.325 0.995/0.990 表 4 不同缺失率下预测模型的平均MAPE
Table 4. Mean MAPE of prediction models under different miss rates
% 预测模型 未填补 填补算法 RF KNN DT PSO−SVR PSO−RF 7.7 4.8 5.6 4.05 5.5 PSO−XGBoost 8.3 5.6 6.7 4.50 6.3 PSO−SVR 7.0 3.9 5.1 4.04 4.8 -
[1] 邓军,白祖锦,肖旸,等. 煤自燃灾害防治技术现状与挑战[J]. 煤矿安全,2020,51(10):118-125. doi: 10.13347/j.cnki.mkaq.2020.10.018DENG Jun,BAI Zujin,XIAO Yang,et al. Present situation and challenge of coal spontaneous combustion disasters prevention and control technology[J]. Safety in Coal Mines,2020,51(10):118-125. doi: 10.13347/j.cnki.mkaq.2020.10.018 [2] 王德明,邵振鲁,朱云飞. 煤矿热动力重大灾害中的几个科学问题[J]. 煤炭学报,2021,46(1):57-64. doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.YG20.1798WANG Deming,SHAO Zhenlu,ZHU Yunfei. Several scientific issues on major thermodynamic disasters in coal mines[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2021,46(1):57-64. doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.YG20.1798 [3] 王德明. 煤矿热动力灾害及特性[J]. 煤炭学报,2018,43(1):137-142. doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2017.4300WANG Deming. Thermodynamic disaster in coal mine and its characteristics[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2018,43(1):137-142. doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2017.4300 [4] 郭庆. 采空区煤自燃预警技术及应用研究[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2021.GUO Qing. Research on early warning technology and application of coal spontaneous combustion in goaf[D]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology, 2021. [5] ONIFADE M,GENC B,BADA S. Spontaneous combustion liability between coal seams:a thermogravimetric study[J]. International Journal of Mining Science and Technology,2020,30(5):691-698. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmst.2020.03.006 [6] 邓军,雷昌奎,曹凯,等. 采空区煤自燃预测的随机森林方法[J]. 煤炭学报,2018,43(10):2800-2808. doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2018.0710DENG Jun,LEI Changkui,CAO Kai,et al. Random forest method for predicting coal spontaneous combustion in gob[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2018,43(10):2800-2808. doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2018.0710 [7] DENG Jun,CHEN Weile,WANG Caiping,et al. Prediction model for coal spontaneous combustion based on SA-SVM.[J]. ACS Omega,2021,6(17):11307-11318. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.1c00169 [8] 周旭,朱毅,张九零,等. 基于PSO−XGBoost的煤自燃程度预测研究[J]. 矿业安全与环保,2022,49(6):79-84.ZHOU Xu,ZHU Yi,ZHANG Jiuling,et al. Study on prediction model of coal spontaneous combustion based on PSO-XGBoost[J]. Mining Safety & Environmental Protection,2022,49(6):79-84. [9] 彭志江. 面向小样本数据的特征分析技术研究[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学, 2021.PENG Zhijiang. Feature analysis technology for small sample data[D]. Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2021. [10] 郑晓亮. 基于瓦斯含量法的煤与瓦斯突出预测关键技术研究[D]. 淮南: 安徽理工大学, 2018.ZHENG Xiaoliang. Research on key technology of coal and gas outburst prediction based on gas content method[D]. Huainan: Anhui University of Science and Technology, 2018. [11] 陈娟,王献雨,罗玲玲,等. 缺失值填补效果:机器学习与统计学习的比较[J]. 统计与决策,2020,36(17):28-32. doi: 10.13546/j.cnki.tjyjc.2020.17.006CHENG Juan,WANG Xianyu,LUO Lingling,et al. Comparison of machine learning and statistical learning in the imputation of missing values[J]. Statistics & Decision,2020,36(17):28-32. doi: 10.13546/j.cnki.tjyjc.2020.17.006 [12] 陈利成,陈建宏. 基于数据填补−机器学习的煤与瓦斯突出预测效果研究[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术,2022,18(9):69-74.CHEN Licheng,CHEN Jianhong. Study on prediction effect of coal and gas outburst based on data imputation and machine learning[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology,2022,18(9):69-74. [13] 郑晓亮,来文豪,薛生. MI和SVM算法在煤与瓦斯突出预测中的应用[J]. 中国安全科学学报,2021,31(1):75-80. doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2021.01.011ZHENG Xiaoliang,LAI Wenhao,XUE Sheng. Application of MI and SVM in coal and gas outburst prediction[J]. China Safety Science Journal,2021,31(1):75-80. doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2021.01.011 [14] LI Zhuoxuan,SHI Xinli,CAO Jinde,et al. CPSO-XGBoost segmented regression model for asphalt pavement deflection basin area prediction[J]. Science China (Technological Sciences),2022,65(7):1470-1481. doi: 10.1007/s11431-021-1972-7 [15] 任万兴,郭庆,石晶泰,等. 基于标志气体统计学特征的煤自燃预警指标构建[J]. 煤炭学报,2021,46(6):1747-1758. doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.HZ21.0006REN Wanxing,GUO Qing,SHI Jingtai,et al. Construction of early warning indicators for coal spontaneous combustion based on statistical characteristics of index gases[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2021,46(6):1747-1758. doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.HZ21.0006 -



 下载:
下载: