Mine underground space modeling method based on semantic multi-scale
-
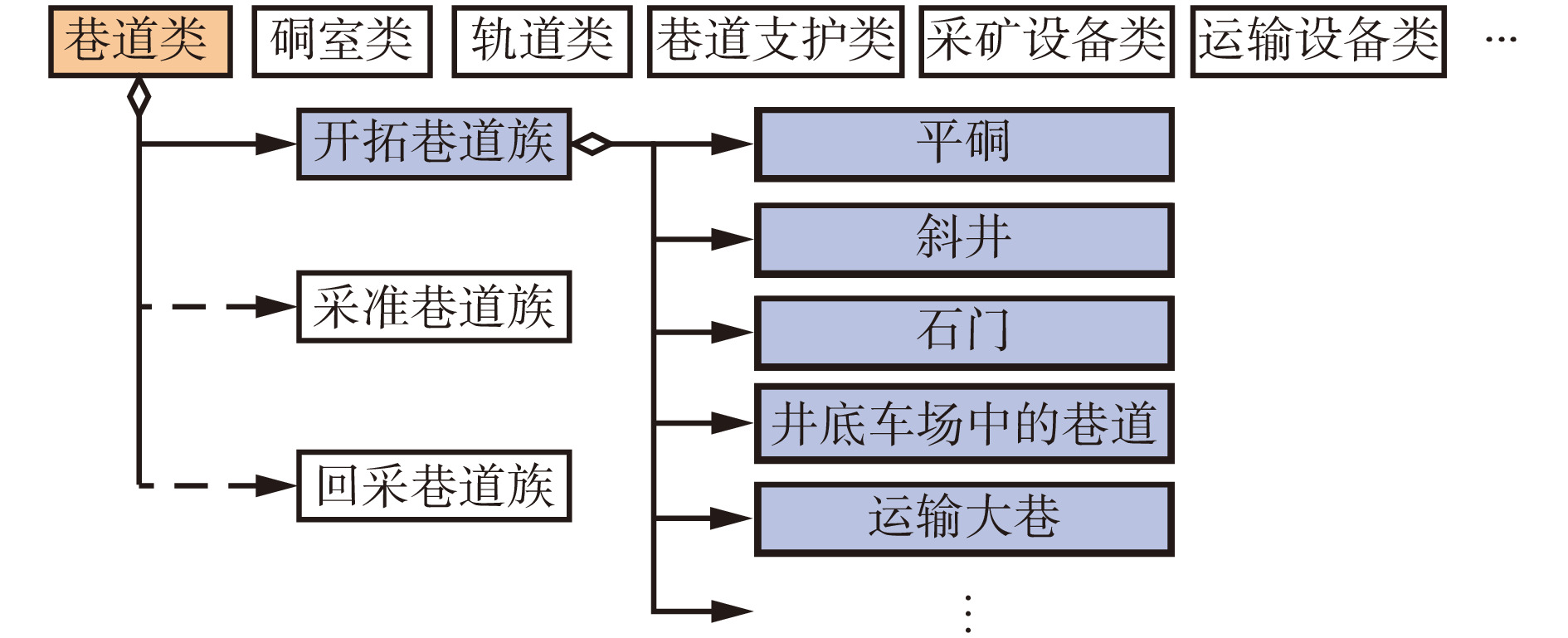
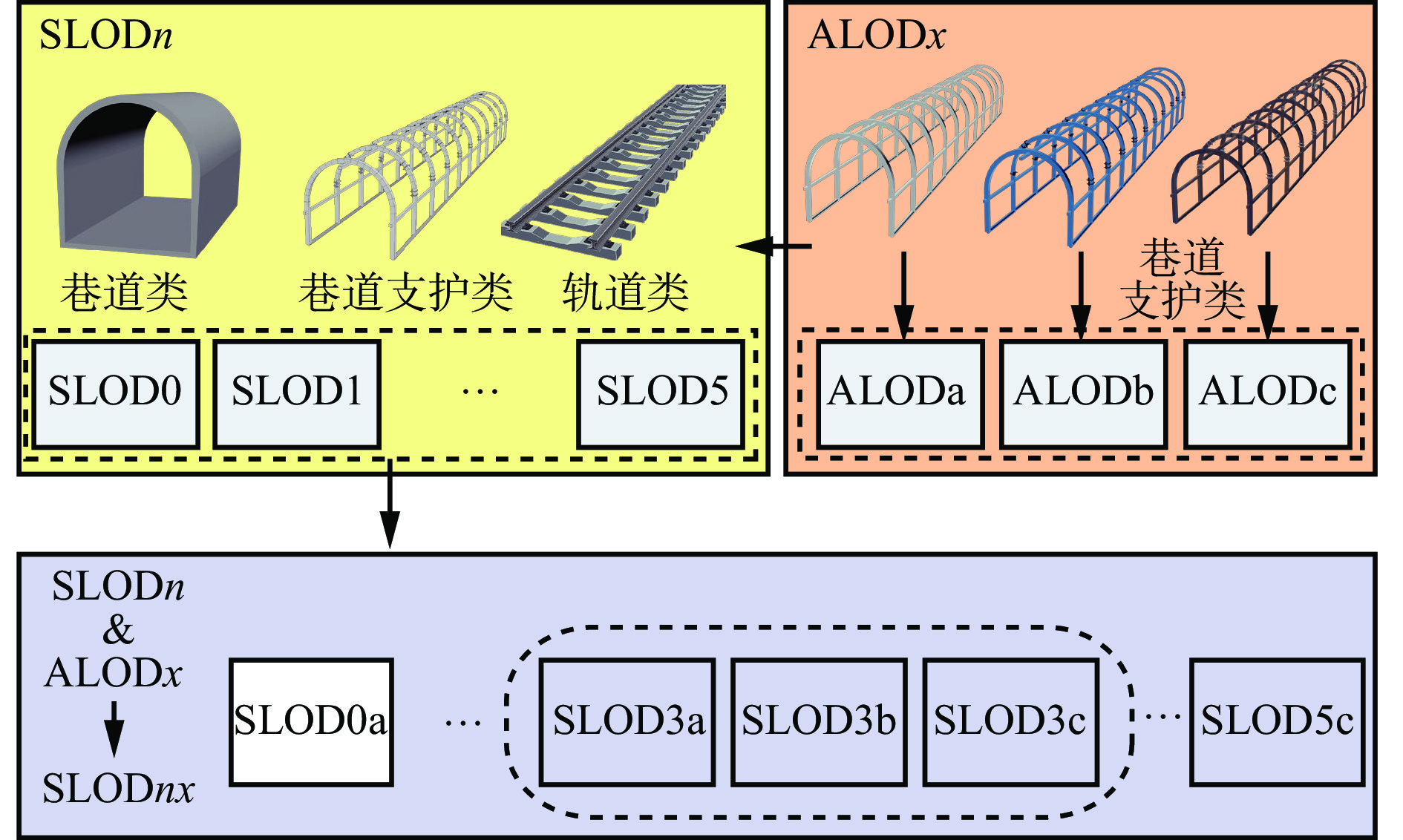
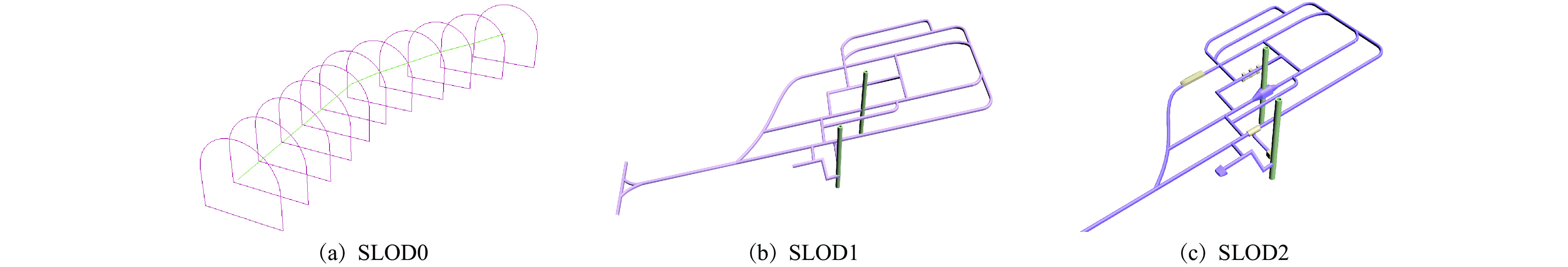
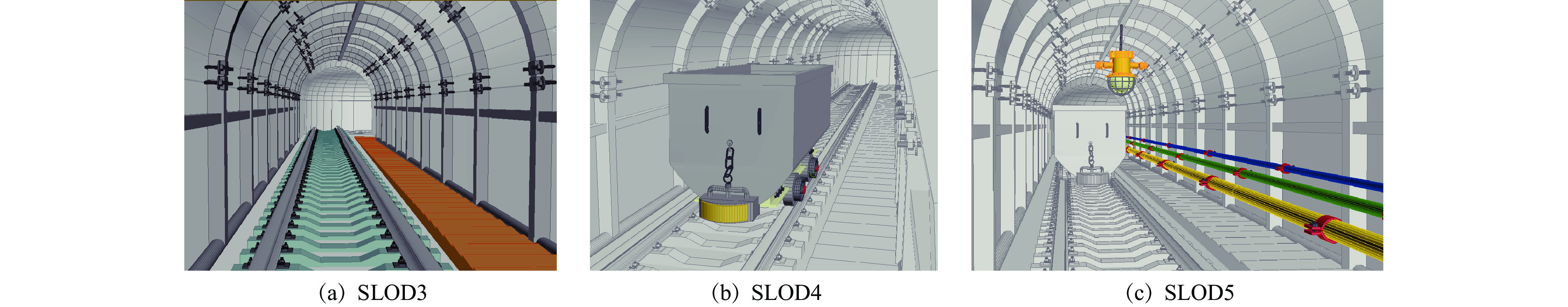
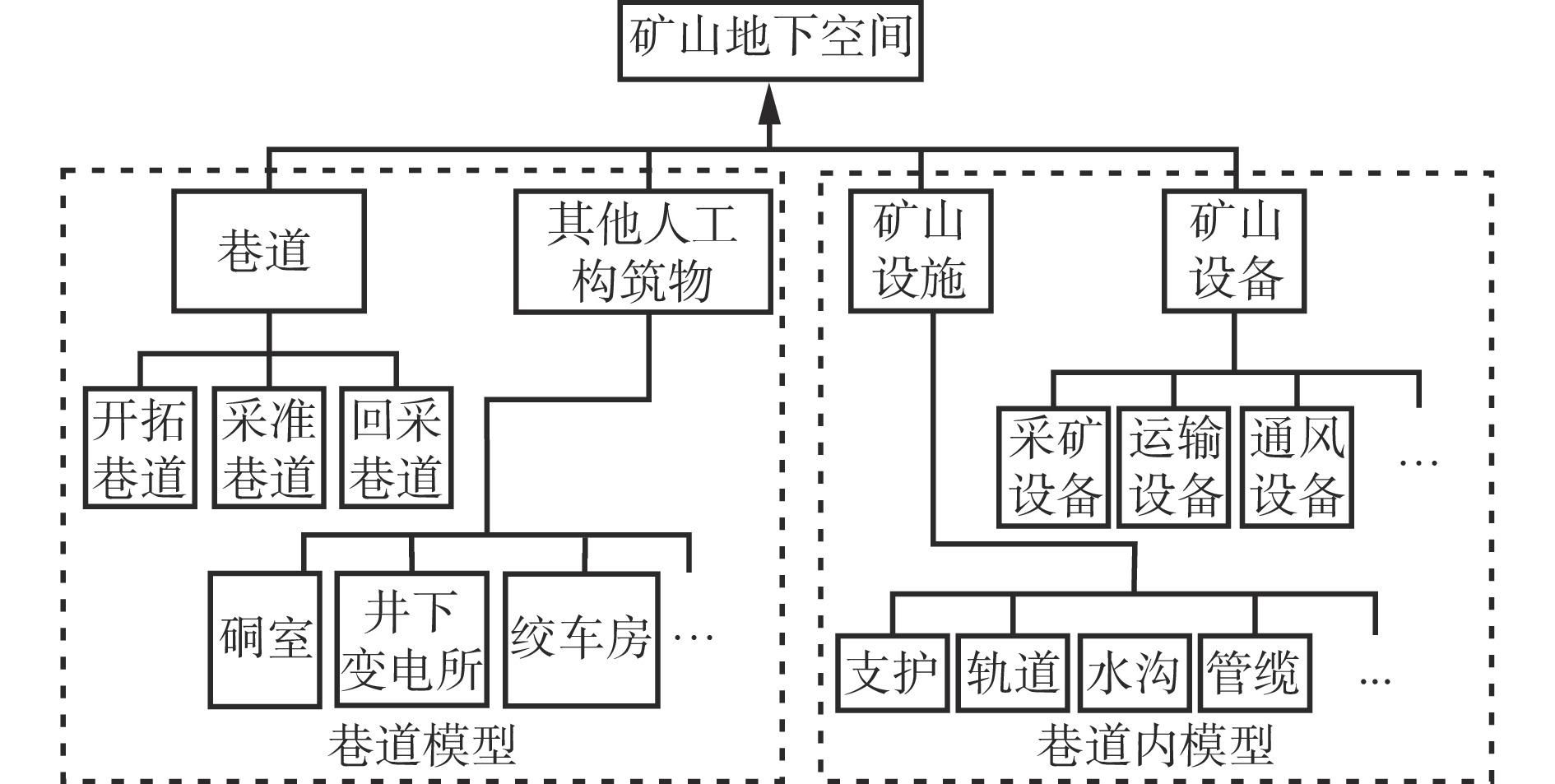
摘要: 针对基于语义的地下矿山实体建模方法细节层次划分不够详细、模型配置自由度较小、缺乏多尺度精细化表达的问题,将参数化建模和语义多尺度思想应用到矿山多细节层次(LOD)模型构建中,提出基于语义多尺度的矿山地下空间建模方法。确定建模对象为矿山地下空间内的实体要素,依据实体要素位置划分为巷道模型和巷道内模型,巷道模型包括巷道主体模型及其他人工构筑物模型,巷道内模型包括矿山设施模型和设备模型;根据实体要素的语义信息定义不同的语义类,语义类向下划分成族,再按照功能将族分解为组件元素;通过语义属性、几何属性、外观属性、特征属性等可量化指标来描述每个语义类。设计了矿山LOD模型,该模型包括6个层次的离散化LOD模型:巷道网络模型、巷道粗略模型、巷道精细模型、巷道内主要设施模型、巷道内主要设备模型、巷道内其他设备模型,将离散化LOD模型与各种属性进行组合,可清晰显示矿山LOD模型的详细程度和主次关系。基于语义多尺度的矿山地下空间建模方法能够提供不同细节丰富度的实体要素模型,降低场景渲染的计算复杂度,提高模型构建的效率和灵活性。Abstract: In order to solve the problems of semantic-based underground mine entity modeling method, such as the lack of detail level division, the small degree of freedom of model configuration, and the lack of multi-scale fine expression, parametric modeling and semantic multi-scale ideas are applied to the construction of mine multi-level of detail (LOD) model, and a mine underground space modeling method based on semantic multi-scale is proposed. It is determined that the modeling object is the entity element in mine underground space. The modeling objects are divided into roadway model and in-roadway model according to the position of the entity element. The roadway model comprises a roadway main body model and other artificial structure models, and the in-roadway model comprises a mine facility model and an equipment model. The different semantic classes are defined according to the semantic information of the entity elements. The semantic classes are divided into families, and then the families are decomposed into component elements according to their functions. Each semantic class is described by quantifiable indicators such as semantic attributes, geometric attributes, appearance attributes and characteristic attributes. The mine LOD model is designed, which includes six levels of discrete LOD models, namely roadway network model, roadway rough model, roadway fine model, main facility model in roadway, main equipment model in roadway, and other equipment models in roadway. Combining the discrete LOD model with various attributes can clearly show the level of detail and the primary and secondary relationships of the mine LOD model. The mine underground space modeling method based on semantic multi-scale can provide entity element models with different detail richness, reduce the computational complexity of scene rendering and improve the efficiency and flexibility of model construction.
-
Keywords:
- mine 3D modeling /
- parametric modeling /
- semantic multi-scale /
- LOD /
- semantic division /
- fine expression
-
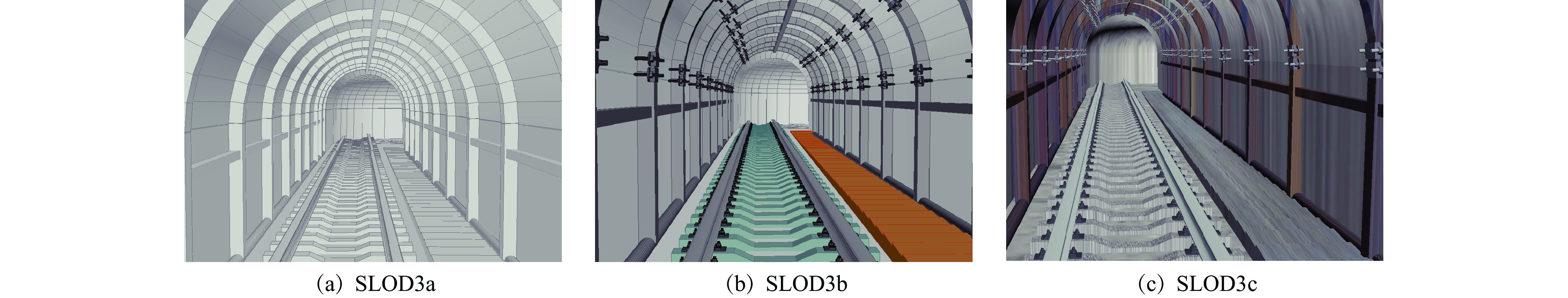
表 1 巷道和巷道内SLOD和ALOD组合
Table 1 Combination of SLOD and ALOD of roadway and in-roadway
SLODn SLODnx ALODa ALODb ALODc SLOD0 SLOD0a × × SLOD1 SLOD1a SLOD1b SLOD1c SLOD2 SLOD2a SLOD2b SLOD2c SLOD3 SLOD3a SLOD3b SLOD3c SLOD4 SLOD4a SLOD4b SLOD4c SLOD5 SLOD5a SLOD5b SLOD5c -
[1] 谷保泽,邱少杰. 透明化矿山建设关键技术探讨[J]. 工矿自动化,2021,47(增刊1):24-25. GU Baoze,QIU Shaojie. Discussion on key technologies for transparent mine construction[J]. Industry and Mine Automation,2021,47(S1):24-25.
[2] 张珂,杨应迪,刘学通,等. 矿井通风系统三维模型的构建与应用[J]. 工矿自动化,2020,46(2):59-64. ZHANG Ke,YANG Yingdi,LIU Xuetong,et al. Construction and application of three-dimensional model of mine ventilation system[J]. Industry and Mine Automation,2020,46(2):59-64.
[3] LI Wenjing,LI Siyi,LIN Zhiyong,et al. Information modeling of mine working based on BIM technology[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology,2021,115(3):103978.
[4] 张元生. 地上下无缝集成多尺度建模与应用研究[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 2010. ZHANG Yuansheng. Study on aground-underground seamlessly integrated multi-lod modeling and application[D]. Shenyang: Northeastern University, 2010.
[5] BILJECKI F, ZHAO J, STOTER J E, et al. Revisiting the concept level of detail in 3D city modelling[C]//ISPRS 8th 3DGeoInfo Conference & WG II/2 Workshop, Istanbul, 2013: 63-74.
[6] 贾小斌,艾廷华,彭子凤,等. 地理信息语义的LOD表达与相似性度量[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2016,41(10):1299-1306. JIA Xiaobin,AI Tinghua,PENG Zifeng,et al. The LOD representation and proximity measurement of semantic about geographic information[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2016,41(10):1299-1306.
[7] BILJECKI F,LEDOUX H,STOTER J,et al. Formalisation of the level of detail in 3D city modelling[J]. Computers,Environment and Urban Systems,2014,48:1-15. DOI: 10.1016/j.compenvurbsys.2014.05.004
[8] BILJECKI F,LEDOUX H,STOTER J. An improved LOD specification for 3D building models[J]. Computers,Environment and Urban Systems,2016,59:25-37. DOI: 10.1016/j.compenvurbsys.2016.04.005
[9] SARAN S,OBERAI K,WATE P,et al. Utilities of virtual 3D city models based on CityGML:Various use cases[J]. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing,2018,46(6):957-972. DOI: 10.1007/s12524-018-0755-5
[10] TANG Lei,YING Shen,LI Lin,et al. An application-driven LOD modeling paradigm for 3D building models[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing,2020,161:194-207. DOI: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2020.01.019
[11] 熊书敏. 地下矿生产可视化管控系统关键技术研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2012. XIONG Shumin. Study on key technologies of underground mine production 3D visual management and control system[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2012.
[12] 李雯静,陈曼丽,任大军. 句法视角下矿山地下空间结构研究与优化[J]. 金属矿山,2022(1):154-161. LI Wenjing,CHEN Manli,REN Dajun. Study and optimization of mine underground space structure from syntax perspective[J]. Metal Mine,2022(1):154-161.
[13] RADANOVIC M,KHOSHELHAM K,FRASER C. Geometric accuracy and semantic richness in heritage BIM:A review[J]. Digital Applications in Archaeology and Cultural Heritage,2020,19:e00166. DOI: 10.1016/j.daach.2020.e00166
[14] 李雯静, 张馨心, 焦宇豪. 基于精细拓扑的矿井排水系统多尺度建模[J/OL]. 金属矿山: 1-9[2022-03-11]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/34.1055.TD.20211021.1117.002.html. LI Wenjing, ZHANG Xinxin, JIAO Yuhao. Multi-scale modeling of mine drainage system based on detailed topological structure[J/OL]. Metal Mine: 1-9[2022-03-11]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/34.1055.TD.20211021.1117.002.html.
[15] 李江. 基于语义尺度的矿山多模型构建与不确定性研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学, 2016. LI Jiang. Research approach for multiple sequence of three-dimensional models of mine based on semantic scale and uncertain analysis on geology modeling[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, 2016.
[16] 李雯静, 焦宇豪, 邱莉, 等. 基于Dynamo的矿井巷道参数化建模[J/OL]. 金属矿山: 1-11[2022-03-11]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/34.1055.TD.20210705.1602.004.html. LI Wenjing, JIAO Yuhao, QIU Li, et al. Parametric modeling of mine roadway based on Dynamo[J/OL]. Metal Mine: 1-11[2022-03-11]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/34.1055.TD.20210705.1602.004.html.
[17] 谢景龙,张得群. 矿山三维巷道的参数化建模及其可视化[J]. 矿山测量,2017,45(5):5-9. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-358X.2017.05.002 XIE Jinglong,ZHANG Dequn. Parametric modeling and visualization of 3D mine laneway[J]. Mine Surveying,2017,45(5):5-9. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-358X.2017.05.002
[18] WANG Guangbin,ZHANG Zhujing. BIM implementation in handover management for underground rail transit project:A case study approach[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology,2021,108:103684. DOI: 10.1016/j.tust.2020.103684
[19] 刘贝. 基于BIM技术的隧道参数化建模及模型应用研究[D]. 青岛: 青岛理工大学, 2019. LIU Bei. Parametric modeling and model application of tunnel based on BIM technology[D]. Qingdao: Qingdao University of Technology, 2019.
[20] WANG Yunjia,FU Yongming,FU Erjiang. On 3D geo-visualization of a mine surface plant and mine roadway[J]. Geo-spatial Information Science,2007,10(4):287-292. DOI: 10.1007/s11806-007-0098-9
[21] LUEBKE D, REDDY M, COHEN J D, et al. Level of detail for 3D graphics[M]. San Francisco: Morgan Kaufmann, 2003.
[22] ZHU Qing,ZHAO Junqiao,DU Zhiqiang,et al. Quantitative analysis of discrete 3D geometrical detail levels based on perceptual metric[J]. Computers & Graphics,2010,34(1):55-65.
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 马宏伟,孙思雅,王川伟,毛清华,薛旭升,刘鹏,田海波,王鹏,张烨,聂珍,马柯翔,郭逸风,张恒,王赛赛,李烺,苏浩,崔闻达,成佳帅,喻祖坤. 论“掘进就是掘模型”的学术思想. 煤炭学报. 2025(01): 661-675 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 任宁,贾皓然,刘航序. 人防工程中基于BIM技术的地下空间管线廊道管理方法. 建筑安全. 2023(07): 4-8 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)



 下载:
下载: