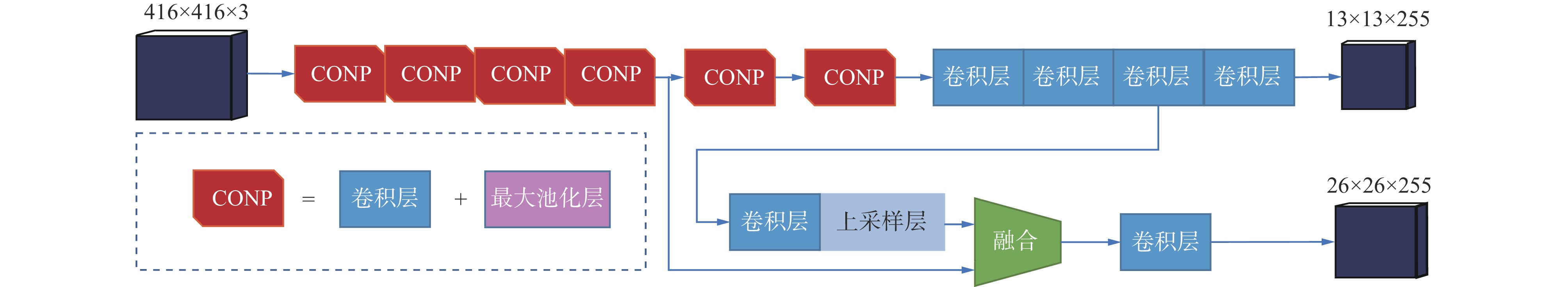
An improved tiny YOLO v3 rapid recognition model for coal-gangue
-
摘要: 传统的煤矸石分选方法效率低下、安全隐患较大、应用范围受限,现有的基于机器视觉的煤矸石图像识别方法在模型识别速度与精度上难以平衡,未综合考虑输入图像尺寸不一、重要通道权重较低及卷积参数量大对模型精度的影响。针对上述问题,在tiny YOLO v3模型的基础上,提出了一种改进的tiny YOLO v3煤矸石快速识别模型。首先,在tiny YOLO v3模型引入多卷积核组合池化的特征金字塔池化(SPP)网络,确保输入特征图可被处理为固定尺寸再输出;其次,引入RGB通道权重可调节的压缩激励(SE)模块,用于增强前几层特征图各通道之间的联系,强调感兴趣通道的特征值和不同目标特征之间的差异性,确保关键信息的捕捉和网络灵敏度;最后,引入包含0权值点的空洞卷积替代tiny YOLO v3模型中部分卷积层,在不增加模型参数的前提下,可捕获多尺度上下文信息进而扩大感受野,提高模型计算速度。将该模型分别与tiny YOLO v3模型、Faster RCNN模型、YOLO v5系列模型进行对比,结果表明:① 与tiny YOLO v3相比,改进的tiny YOLO v3煤矸石快速识别模型的识别准确性和快速性都有显著提升。② 与Faster RCNN相比,改进的tiny YOLO v3煤矸石快速识别模型训练时间减少了65.72%,识别精度增幅为11.83%,识别召回率增幅为0.5%,模型平均精度均值(mAP)增幅为3.02%。③ 与YOLO系列模型相比,改进的tiny YOLO v3煤矸石快速识别模型在保持识别精度优势的情况下识别速度有大幅增长。消融实验结果表明:改进的tiny YOLO v3煤矸石快速识别模型的识别准确率为99.4%,较加入SPP网络的tiny YOLO v3模型的识别准确率提高了4.9%;测试每张图片耗时12.5 ms,较加入SPP网络的tiny YOLO v3模型耗时减少了1 ms。Abstract: The traditional coal gangue sorting methods have low efficiency, significant safety hazards, and limited application scope. The existing machine vision-based coal gangue image recognition methods are difficult to balance model recognition speed and accuracy. And the methods do not comprehensively consider the impact of different input image sizes, low important channel weights, and large convolution parameters on model precision. In order to solve the above problems, an improved tiny YOLO v3 coal gangue rapid recognition model is proposed based on the tiny YOLO v3 model. Firstly, a spatial pyramid pooling (SPP) network with multiple convolutional kernels combined pooling is introduced in the tiny YOLO v3 model to ensure that the input feature maps can be processed to a fixed size before being output. Secondly, a squeeze-and-excitation (SE) module with adjustable RGB channel weights is introduced to enhance the connections between the channels in the previous layer feature maps. It emphasizes the differences between the feature values of the interested channels and the features of different targets. It ensures the capture of key information and network sensitivity. Finally, the dilated convolution containing zero weight points is introduced to replace part of the convolution layer in the tiny YOLO v3 model. Under the premise of not adding model parameters, multi-scale context information can be captured to expand the receptive field and improve the calculation speed of the model. This model is compared with the tiny YOLO v3 model, Faster RCNN model, and YOLO v5 series models respectively. The results show the following points. ① Compared with tiny YOLO v3, the improved tiny YOLO v3 coal gangue rapid recognition model has significantly improved recognition accuracy and speed. ② Compared with Faster RCNN, the improved tiny YOLO v3 coal gangue rapid recognition model has reduced training time by 65.72%, increased recognition precision by 11.83%, increased recognition recall by 0.5%, and increased model mean average precision (mAP) by 3.02%. ③ Compared with the YOLO series model, the improved tiny YOLO v3 coal gangue rapid recognition model has a significant increase in recognition speed while maintaining the advantage of recognition precision. The results of the ablation experiment show that the improved tiny YOLO v3 coal gangue rapid recognition model has a recognition accuracy of 99.4%. It is 4.9% higher than the tiny YOLO v3 model added with the SPP network. The time to test each image is 12.5 ms, which is 1 ms less than the tiny YOLO v3 model added to the SPP network.
-
表 1 本文模型和Faster RCNN识别数据对比
Table 1. Comparison of identification data between the proposed model and Faster RCNN
% 模型 类别 精确率 召回率 F1 mAP 本文模型 煤 95.3 95.5 97.4 99.4 矸石 97.2 99.9 98.6 Faster RCNN 煤 89.9 94.1 92.0 96.4 矸石 85.7 99.4 92.0 提升 煤 5.67 5.43 5.54 3.02 矸石 11.83 0.5 6.69 表 2 本文模型与YOLOv5系列识别数据对比
Table 2. Comparison between the proposed model and the identification data of YOLOv5 series
模型 识别速度/(帧·s-1) mAP/% YOLO v5s 42.7 96.1 改进YOLO v5s 45.1 98.3 CBA−YOLO 46.7 99.1 本文模型 80 99.4 表 3 各模块消融实验数据对比
Table 3. Comparison of ablation data of each module
改进策略 准确率/% 每张图片耗时/ms SE模块 空洞卷积 × × 94.5 13.5 √ × 97.3 14.1 × √ 96.7 10.9 √ √ 99.4 12.5 -
[1] 曹现刚,李莹,王鹏,等. 煤矸石识别方法研究现状与展望[J]. 工矿自动化,2020,46(1):38-43.CAO Xiangang,LI Ying,WANG Peng,et al. Research status of coal-gangue identification method and its prospect[J]. Industry and Mine Automation,2020,46(1):38-43. [2] 张新. 基于LoRa技术的煤矿作业环境实时监测系统设计[J]. 自动化仪表,2019,40(3):69-73. doi: 10.16086/j.cnki.issn1000-0380.2018080051ZHANG Xin. Design of real-time monitoring system based on LoRa technology for coal mine operation environment[J]. Process Automation Instrumentation,2019,40(3):69-73. doi: 10.16086/j.cnki.issn1000-0380.2018080051 [3] 郭秀军. 煤矸石分选技术研究与应用[J]. 煤炭工程,2017,49(1):74-76. doi: 10.11799/ce201701022GUO Xiujun. Research and application of coal gangue separation technology[J]. Coal Engineering,2017,49(1):74-76. doi: 10.11799/ce201701022 [4] MOHANTA K S,MEIKAPB C. Influence of medium particle size on the separation performance of an air dense medium fluidized bed separator for coal cleaning[J]. Journal of the Southern African Institute of Mining and Metallurgy,2015,115(8):761-766. [5] 陈岩. 基于多元化应用的煤矸石高效破碎分选技术研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉理工大学, 2015.CHEN Yan. Research on efficient crushing and separating technology of coal gangue based on diversified application[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Technology, 2015. [6] 高新宇. 基于机器视觉的煤矸智能分选系统设计[D]. 太原: 太原理工大学, 2021.GAO Xinyu. Design of intelligent separation system for coal and gangue based on machine vision[D]. Taiyuan: Taiyuan University of Technology, 2021. [7] 王征,潘红光. 基于改进差分进化粒子群的煤尘颗粒图像辨识[J]. 煤炭学报,2020,45(2):695-702. doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2019.0074WANG Zheng,PAN Hongguang. Recognition of coal dust image based on improved differential evolution particle swarm optimization[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2020,45(2):695-702. doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2019.0074 [8] 沈科,季亮,张袁浩,等. 基于改进YOLOv5s模型的煤矸目标检测[J]. 工矿自动化,2021,47(11):107-111,118.SHEN Ke,JI Liang,ZHANG Yuanhao,et al. Reserch on coal and gangue detection algorithm based on improved YOLOv5s model[J]. Industry and Mine Automation,2021,47(11):107-111,118. [9] 桂方俊,李尧. 基于CBA−YOLO模型的煤矸石检测[J]. 工矿自动化,2022,48(6):128-133. doi: 10.13272/j.issn.1671-251x.2022020033GUI Fangjun,LI Yao. Coal gangue detection based on CBA-YOLO model[J]. Journal of Mine Automation,2022,48(6):128-133. doi: 10.13272/j.issn.1671-251x.2022020033 [10] LI Dongjun,ZHANG Zhenxin,XU Zhihua,et al. An image-based hierarchical deep learning framework for coal and gangue detection[J]. IEEE Access,2019,7:184686-184699. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2961075 [11] 陈彪,卢兆林,代伟,等. 基于轻量化HPG−YOLOX−S模型的煤矸石图像精准识别[J]. 工矿自动化,2022,48(11):33-38.CHEN Biao,LU Zhaolin,DAI Wei,et al. Accurate image recognition of coal gangue based on Lightweight HPG-YOLOX-S model[J]. Journal of Mine Automation,2022,48(11):33-38. [12] PU Yuanyuan,APEL D B,SZMIGIEL A,et al. Image recognition of coal and coal gangue using a convolutional neural network and transfer learning[J]. Energies,2019,12(9):1735-1742. doi: 10.3390/en12091735 [13] 马致颖. 基于CNN−ELM混合模型的煤矸石图像识别方法研究[D]. 淮南: 安徽理工大学, 2022.MA Zhiying. Research on coal gangue image recognition method based on CNN-ELM hybrid model[D]. Huainan: Anhui University of Science and Technology, 2022. [14] REDMON J, FARHADI A. YOLOv3: an incremental improvement[EB/OL]. [2023-01-08]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1804.02767.pdf. [15] BOCHKOVSKIY A, WANG C Y, LIAO H. YOLOv4: optimal speed and accuracy of object detection[EB/OL]. [2023-01-08]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/2004.10934.pdf. [16] LI Longlong,WANG Zhifeng,ZHANG Tingting. GBH-YOLOv5:ghost convolution with bottleneckCSP and tiny target prediction head incorporating YOLOv5 for PV panel defect detection[J]. Electronics,2023,12(3):561-576. doi: 10.3390/electronics12030561 [17] YU F, KOLTUN V. Multi-scale context aggregation by dilated convolutions[C]. International Conference on Learning Representations, Puerto Rico, 2016: 1-13. [18] REDMON J, DIVVALA S, GIRSHICK R, et al. You only look once: unified, real-time object detection[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, 2016: 779-788. [19] REDMON J, FARHADI A. YOLO9000: better, faster, stronger[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, 2017: 7263-7271. [20] LI Chuyi, LI Lulu, JIANG Hongliang, et al. YOLOv6: a single-stage object detection framework for industrial applications[EB/OL]. [2022-09-07]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/2209.02976.pdf. [21] 张陈晨,靳鸿. 基于改进YOLOv3−tiny的目标检测技术研究[J]. 兵器装备工程学报,2021,42(9):215-218,312. doi: 10.11809/bqzbgcxb2021.09.034ZHANG Chenchen,JIN Hong. Research on target detection based on improved YOLOv3-tiny[J]. Journal of Ordnance Equipment Engineering,2021,42(9):215-218,312. doi: 10.11809/bqzbgcxb2021.09.034 -




 下载:
下载: